Home
Monetize Every Square Foot. .
Every underused space is costing you money, every single day.
That spare desk, quiet floor, or unused corner could be earning right now.
With soCommercial.com, turn your space into income in minutes.
From a single desk to an entire building, rent by the hour, day, or month.
You’re in control, you set the price and terms, you deal direct, no middleman.
Just imagine:
A bar today, a co-working space tomorrow
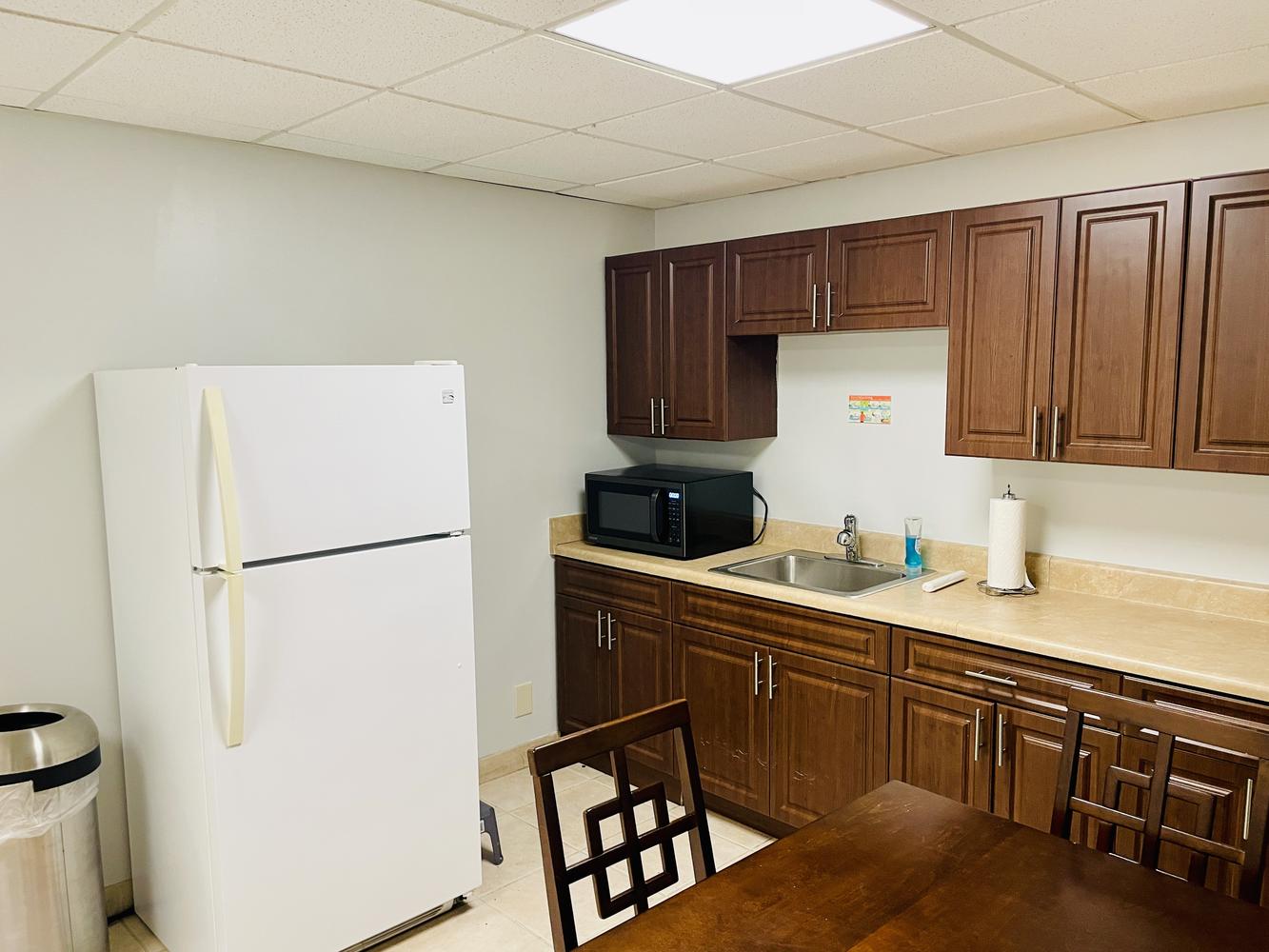
A basement today, a storage space tomorrow
A retail unit today, a pop-up store tomorrow
Every square foot is potential revenue.
Start earning today, every wasted day is lost income.
Need space? We’ll bring it to you.
Tell us what you’re after and Find Space 4 Me finds it fast.
No stress. No scroll. Just great matches, straight to your inbox.
Warning –very catchy jingle & will stay with you day and night.
“Ding Dang Dong Get your listings on …”
Watch the explainer video
Every underused space is costing you money, every single day.
That spare desk, quiet floor, or unused corner could be earning right now.
With soCommercial.com, turn your space into income in minutes.
From a single desk to an entire building, rent by the hour, day, or month.
You’re in control, you set the price and terms, you deal direct, no middleman.
Just imagine:
A bar today, a co-working space tomorrow
A basement today, a storage space tomorrow
A retail unit today, a pop-up store tomorrow
Every square foot is potential revenue.
Start earning today, every wasted day is lost income.
Need space? We’ll bring it to you.
Tell us what you’re after and Find Space 4 Me finds it fast.
No stress. No scroll. Just great matches, straight to your inbox.
Warning –very catchy jingle & will stay with you day and night.
“Ding Dang Dong Get your listings on …”
Watch the explainer video
Omaha, Nebraska, 68144
Size: 1,200 - 120,000 sq. ft.
Price: $10 - $22 per sq. ft. per annum
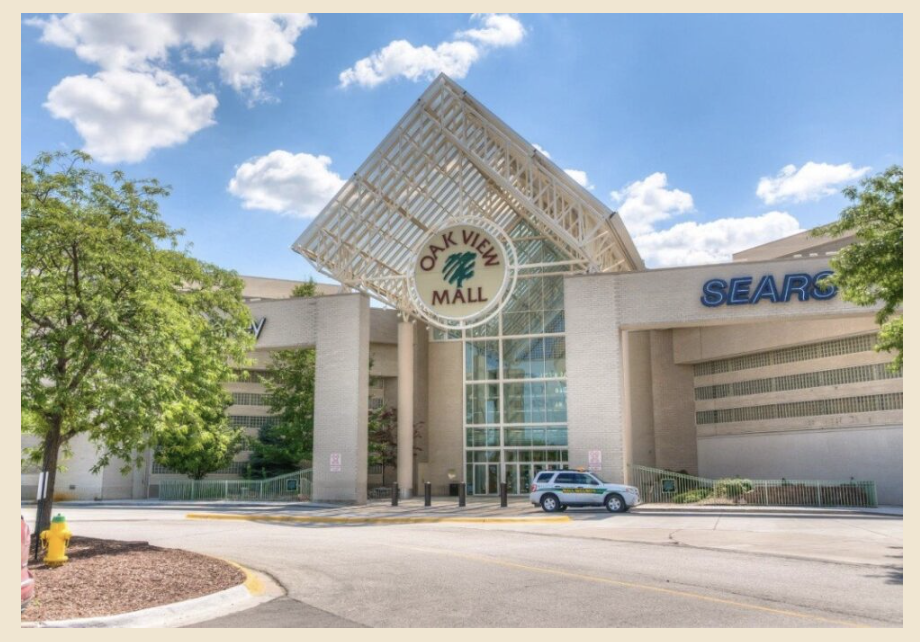
Lease in iconic mall
Redefining Destinations – Lease in a Space Built for Innovation & Engagement! The Mall is a prime investment and leasing opportunity focused on upscale retail, entertainment, and lifestyle experiences. With recent new tenant commitments, the property is experiencing increased leasing momentum, making it an ideal time for retailers, entertainment venues, and experiential brands to secure space. Positioned in a high-income trade area, the Mall is set to become a revitalized shopping, dining, and entertainment hub.
Key Highlights
Strong Demographics: High-income households & strong consumer spending.
Retail & Entertainment Destination: Ideal for fashion, dining, fitness, and luxury brands.
Leasing Momentum: New tenant signings increasing demand.
Experience-Driven Strategy: Focus on entertainment, fitness, and unique retail concepts.
Proximity to Major Employers: High daily foot traffic potential.
- Custom
We offer incentives based on square footage rented, we can offer free rent depending on lease, size and type of business.
- Rent
Discounted rents possible tailored to type of business and length of lease.
- Service Charges
Possible service charge discounts to eligible businesses.
Incentives

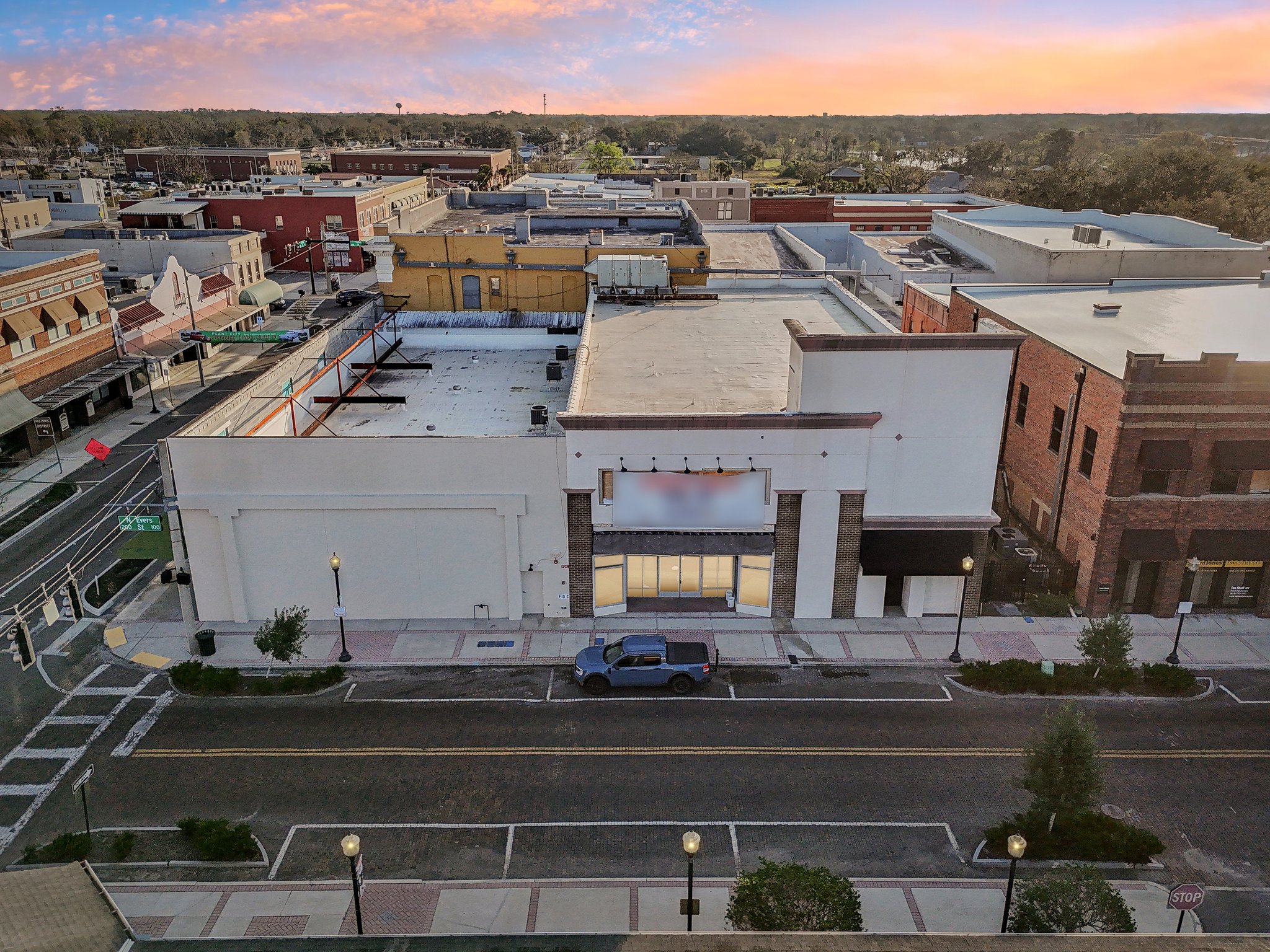
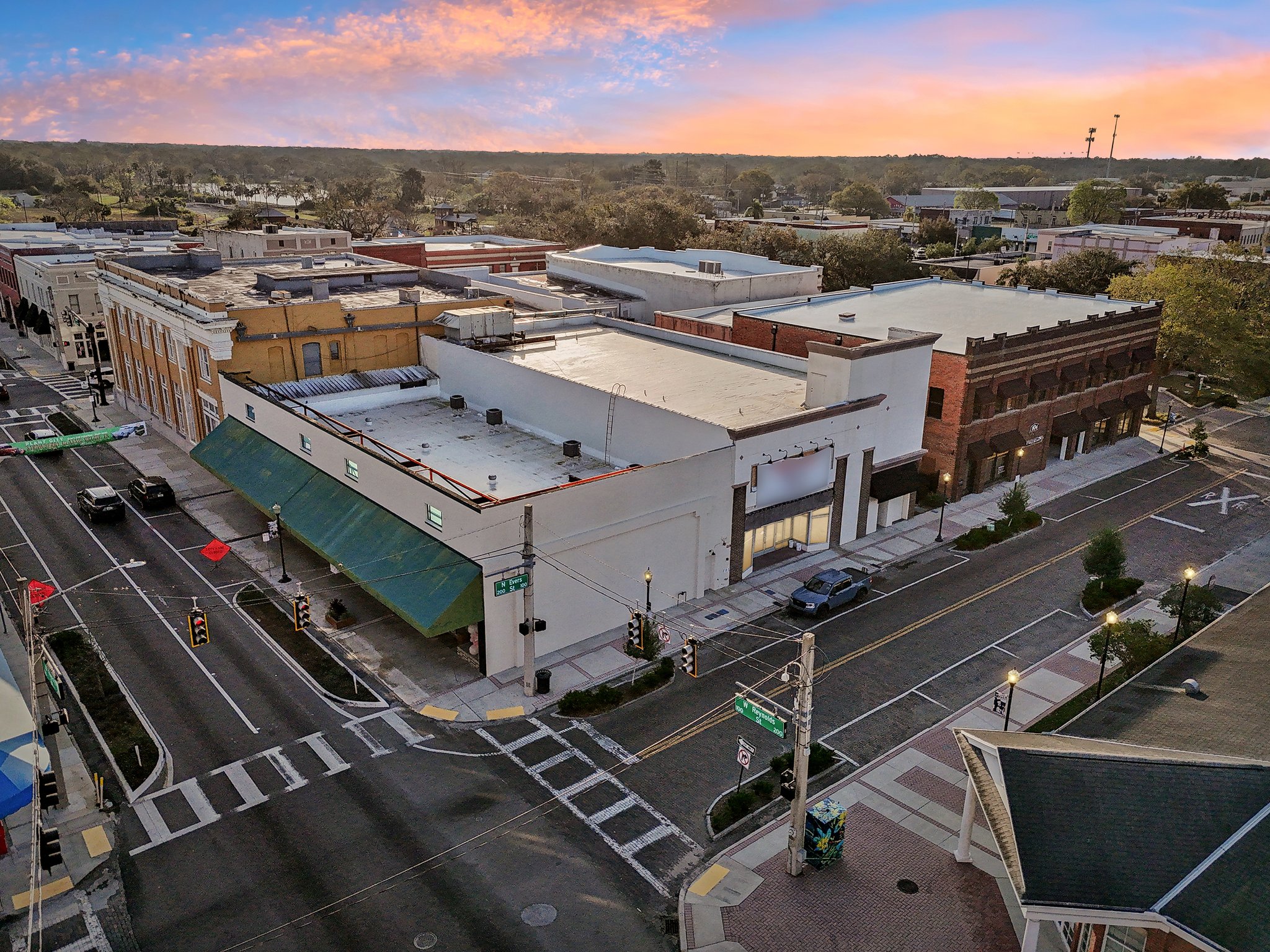
106 N Evers St, Plant City, Florida, 33563
Size: 300 - 11,000 sq. ft.
Price: $15 - $25 per sq. ft. per annum
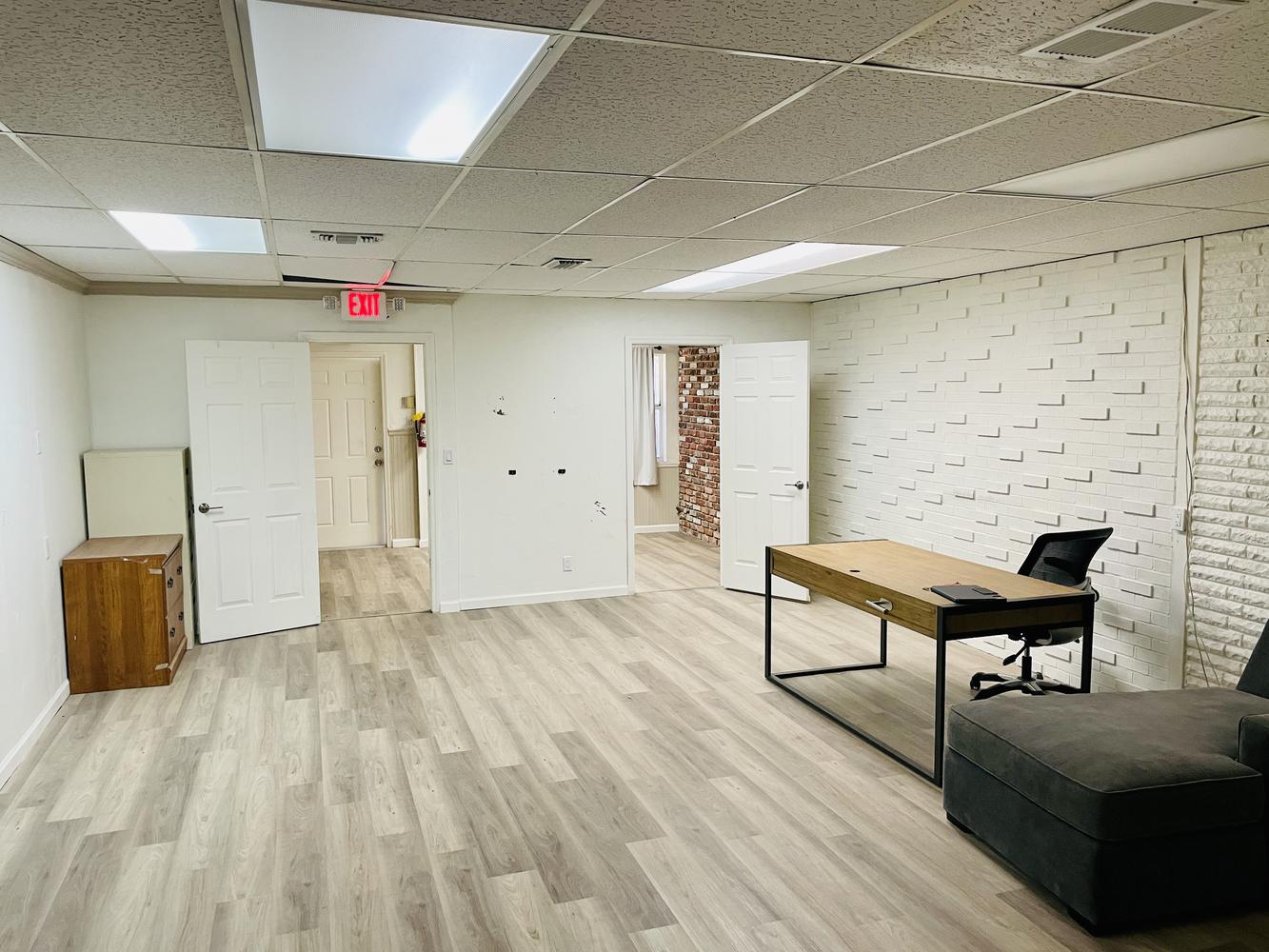
Downtown professional
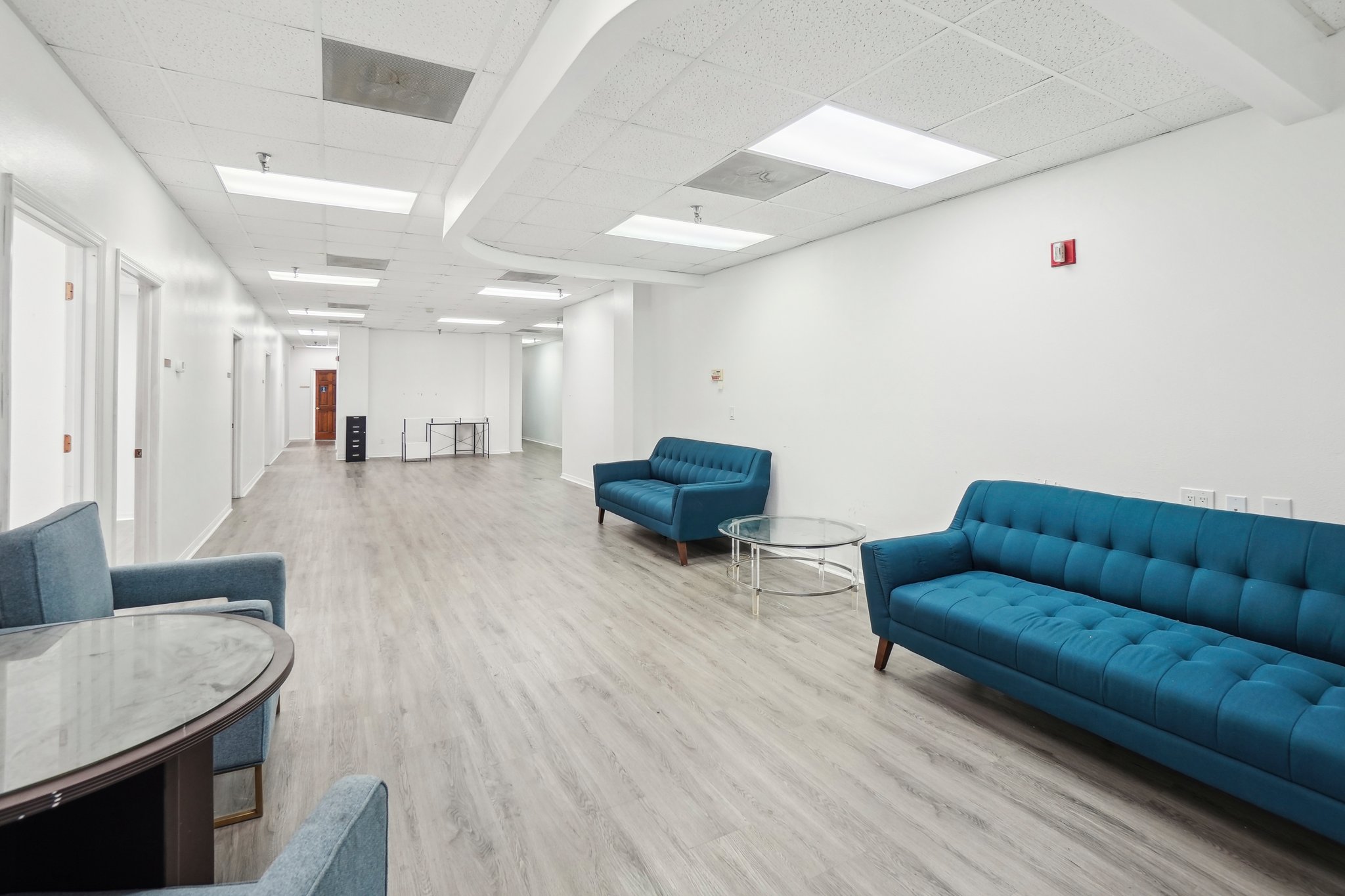
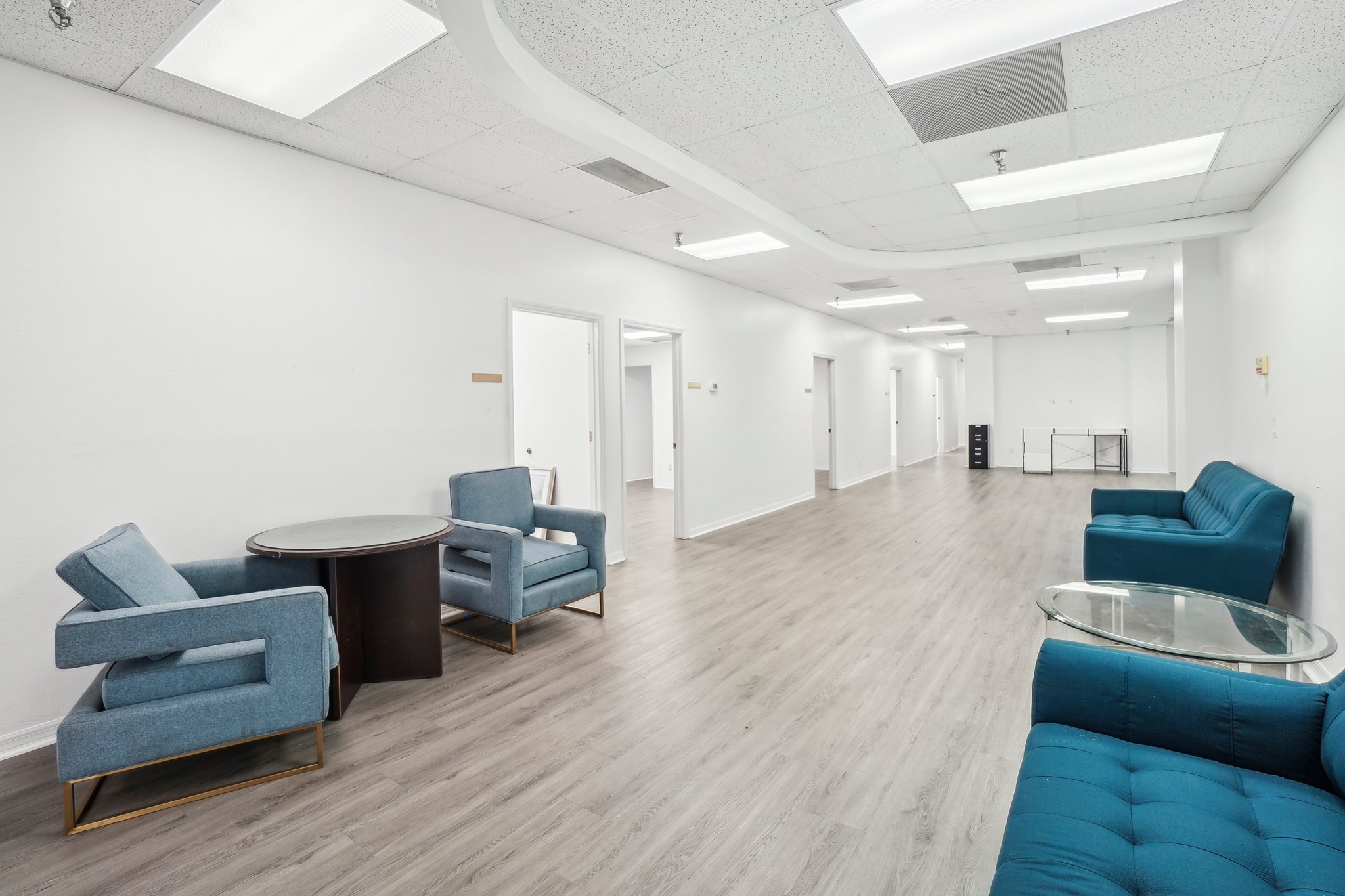
🌟 Versatile Office & Retail Space in the Heart of Plant City
This 11,000 SF flexible commercial space is perfect for a variety of business uses, including professional offices, medical offices, retail, last-mile e-commerce, and coworking operations. Located in a high-visibility area with excellent accessibility, this property offers a modern and adaptable layout to meet the needs of growing businesses.
🔹 Key Features:
✅ Flexible Use – Ideal for professional services, medical, retail, or e-commerce fulfillment.
✅ Prime Location – Centrally located with high foot traffic and visibility.
✅ Spacious & Adaptable Layout – Open floor plan with potential for private offices or collaborative workspaces.
✅ Convenient street parking for staff and clients.
✅ High-Speed Connectivity – Ready for tech-driven businesses and coworking operators.
💼 Perfect For:
✔ Professional Services & Corporate Offices
✔ Medical & Wellness Practices
✔ Retail Showroom & Customer-Facing Businesses
✔ Last-Mile E-commerce & Fulfillment Center
✔ Coworking & Shared Workspace Operators
📞 Schedule a tour today to explore this exceptional leasing opportunity in Plant City!
- Custom
Discounts available for long term leases (5 y plus) for the whole property. Possibility to sublease for co-working operators.
- Rent
Possible discounts.
- Service Charges
Possible discounts.
Incentives

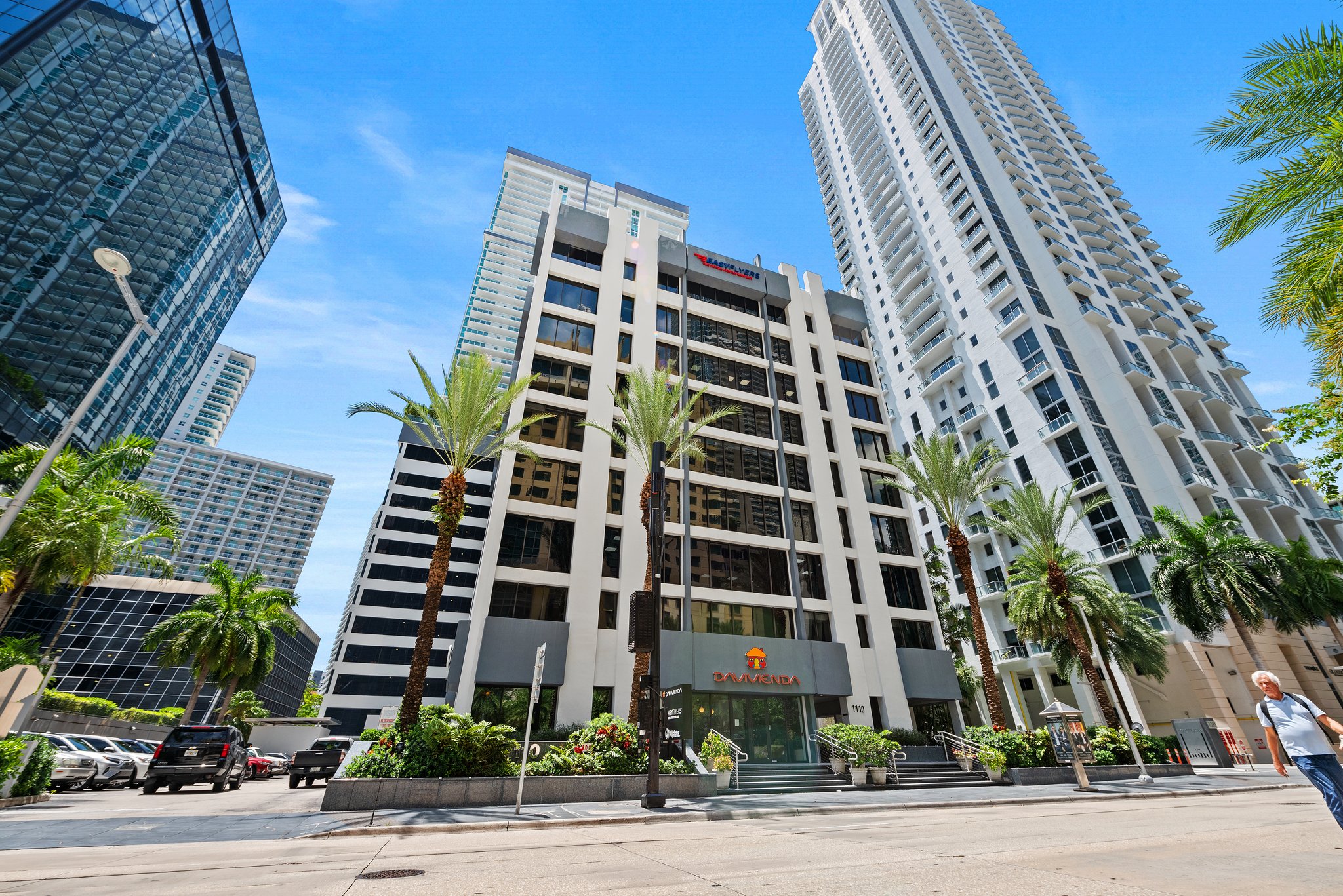
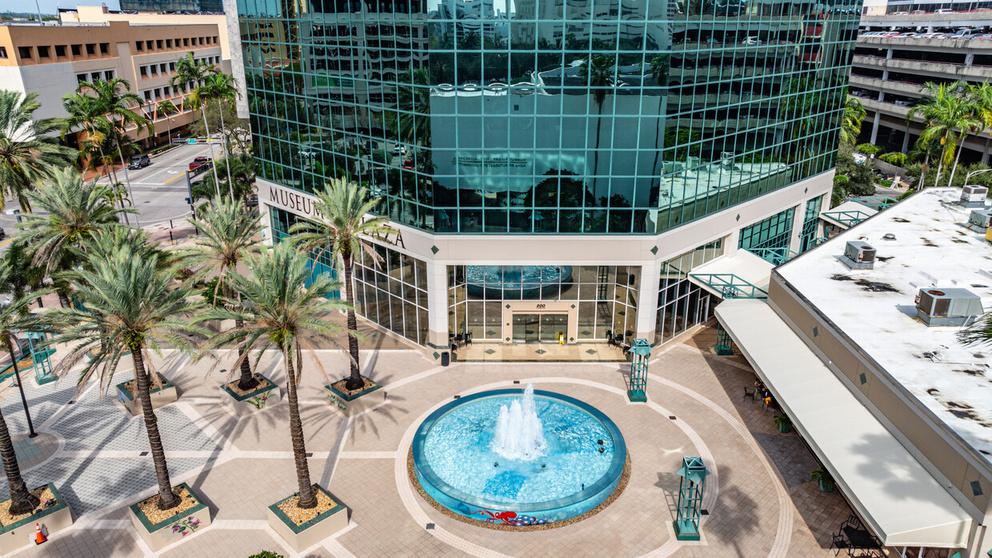
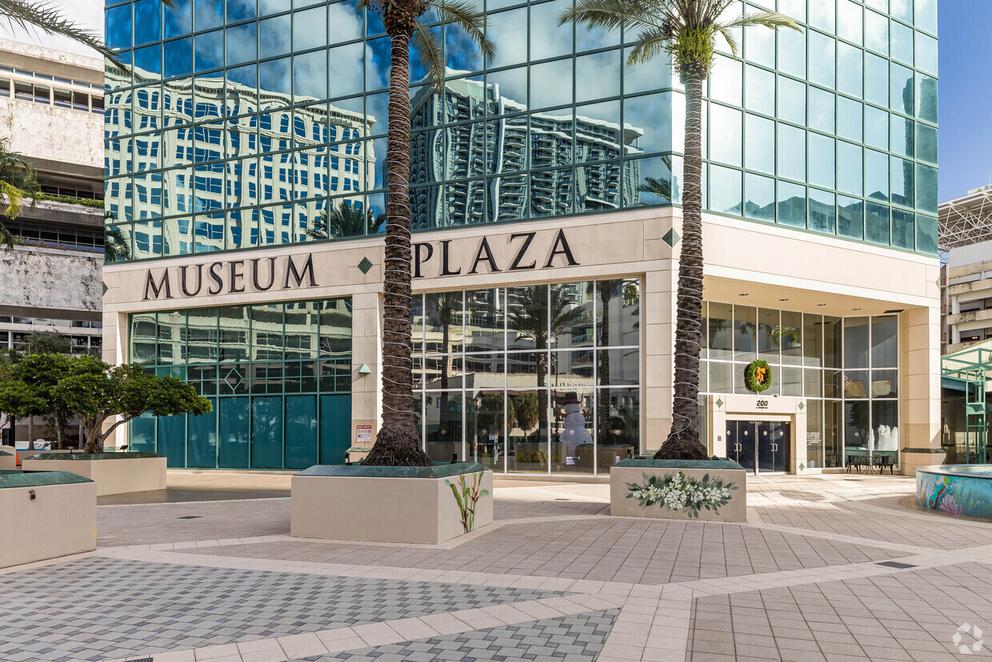
200 South Andrews Avenue, Unit 201, Broward County, Florida, 33301
Size: 5,675 sq. ft.
Price: $1,800,000
Museum Plaza 2nd Floor
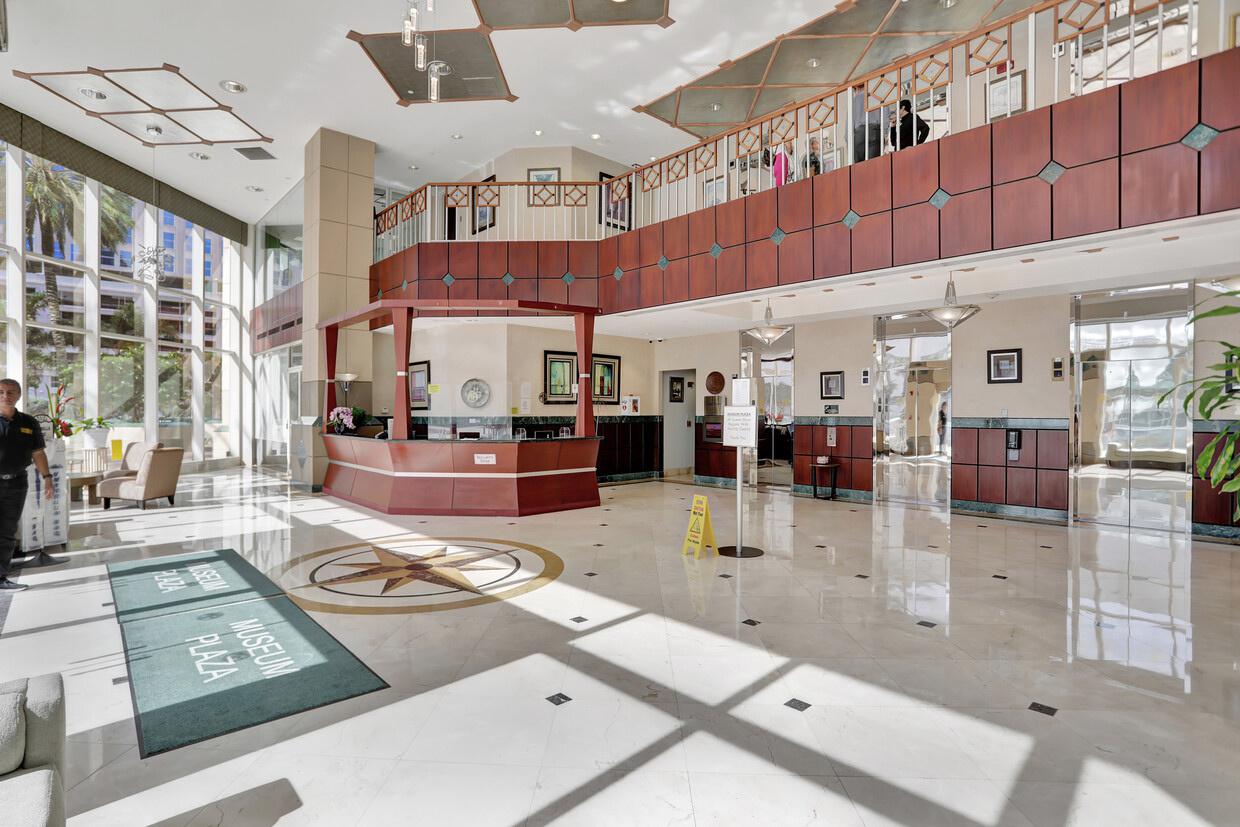
Discover a unique opportunity on the second floor of Museum Plaza on Las Olas, 200 S Andrews Avenue – a Class A office space in the vibrant heart of Downtown Fort Lauderdale, Florida. Perfectly positioned in the city's financial district, just a block from Las Olas Blvd, adjacent to Broward County Government, the local library, and the art museum, it's also close to local and federal courthouses, and FAU and Broward College campuses.
This 11-story building offers interior spaces flooded with natural light through expansive windows and features an impressive double-height lobby with elegant granite and marble finishes, and recently upgraded elevators.
Convenient amenities include a municipal parking garage with EV charging stations and a unique rooftop helicopter pad next door.
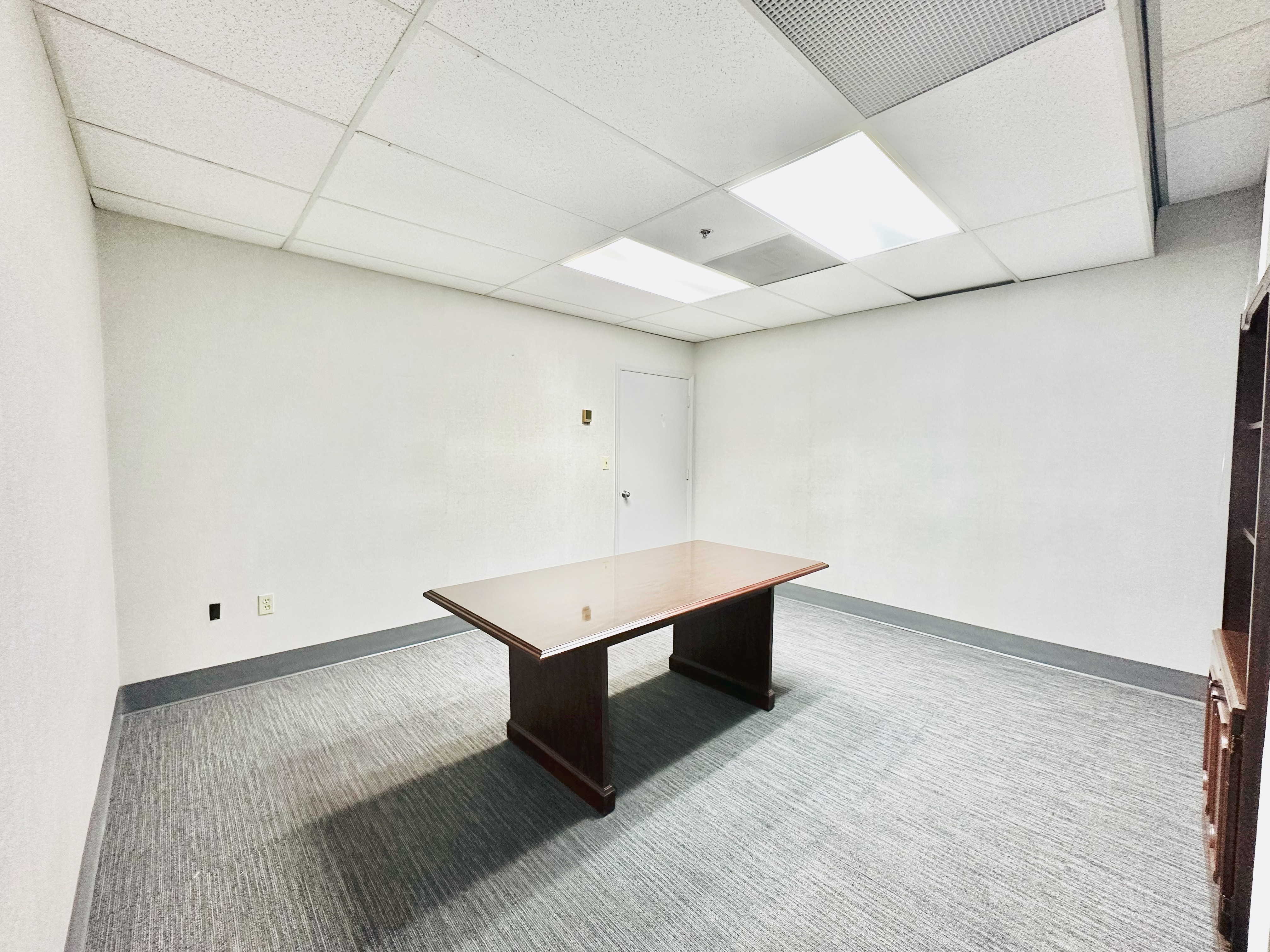
Available for lease or purchase (lease with an option to buy will be considered). the unit offers private offices with floor to ceiling windows along the sides of the unit and an open space with wood like floors in the center. This space is ideal for law firms, accounting offices, or other professional entities, including light medical use. It includes 10 offices and one conference room.
This unit has 3 access doors and WI-FI access to CAT 5 & 6 as well as optic-fiber.
An unmatched opportunity in downtown Fort Lauderdale.
Unit 201 Virtual Tour: https://vrtourhosts.com/listing/65948
Car Charging stations in covered garage
Excellent Location
24 Hr Security

ste 114, ste 114, North Miami, Florida, 33160
Size: 1,600 sq. ft.
Price: Upon application
Ballroom Dance Studio
Ballroom Dance Studio with wooden floors and with integrated music system and mirrors , with spring floors and with warm atmosphere.

200 S Andrews ave, Suites 300-303, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, 33301
Size: 11,563 sq. ft.
Price: $3,500,000
Office Space Museum Plaza-Las Olas
Discover a unique opportunity on the third floor of Museum Plaza on Las Olas, 200 S Andrews Avenue –a Class A office space in the vibrant heart of Downtown Fort Lauderdale, Florida. Perfectly positioned in the city's financial district, just a block from Las Olas Blvd, adjacent to Broward County Government, the local library, and the art museum, it's also close to local and federal courthouses, and FAU and Broward College campuses.
This 11-story building offers interior spaces flooded with natural light through expansive windows and features an impressive double-height lobby with elegant granite and marble finishes, and recently upgraded elevators.
Convenient amenities include a municipal parking garage with EV charging stations and a unique rooftop helicopter pad next door.
Available for lease or purchase (lease with an option to buy will be considered), the unit offers a recently updated full floor, complete with modern open-plan office space, polished concrete flooring, and floor-to-ceiling glass windows. This space is ideal for law firms, accounting offices, or other professional entities, including light medical use. The space can be divided to meet specific needs and includes private and shared offices, conference rooms, two kitchen/break areas, and a variety of layouts. Owner will consider dividing to smaller units
This unit has 3 access doors and WI-FI access to CAT 5 & 6 as well as optic-fiber.
An unmatched opportunity in downtown Fort Lauderdale

2202 Van Buren Street, Broward County, Florida, 33020
Size: 20,501 sq. ft.
Price: $3,200,000
VAN BUREN FLATS
PLANS AND PERMITS INCLUDED!
Ready for a 40 unit residential building.
Great potential for investors in fast growing area.
Currently a 5 unit multifamily with 4 month-to-month tenants.

1516 Park Avenue, New York County, New York, 10029
Size: 10,716 sq. ft.
Price: Upon application
RETAIL FOR LEASE
Ideal for large grocery market
• Black-iron vent in place
• Massive signage opportunity at 25 FT tall
• Designated delivery entrance with conveyor belt to lower level
• At the base of a 60-unit residential building
• Ground floor can be subdivided with/without mezzanine
APPROXIMATE SIZE
Ground Floor: 5,775 SF
Mezzanine: 1,925 SF
Lower Level: 3,016 SF
NEIGHBORS
Success Academy, Irving Farm, C-Town Market, Contento,Casablanca Meat Market, Super Gyro
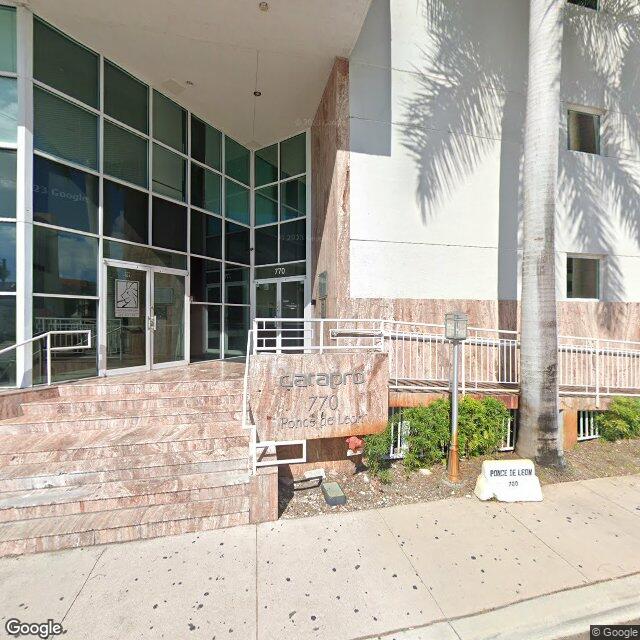
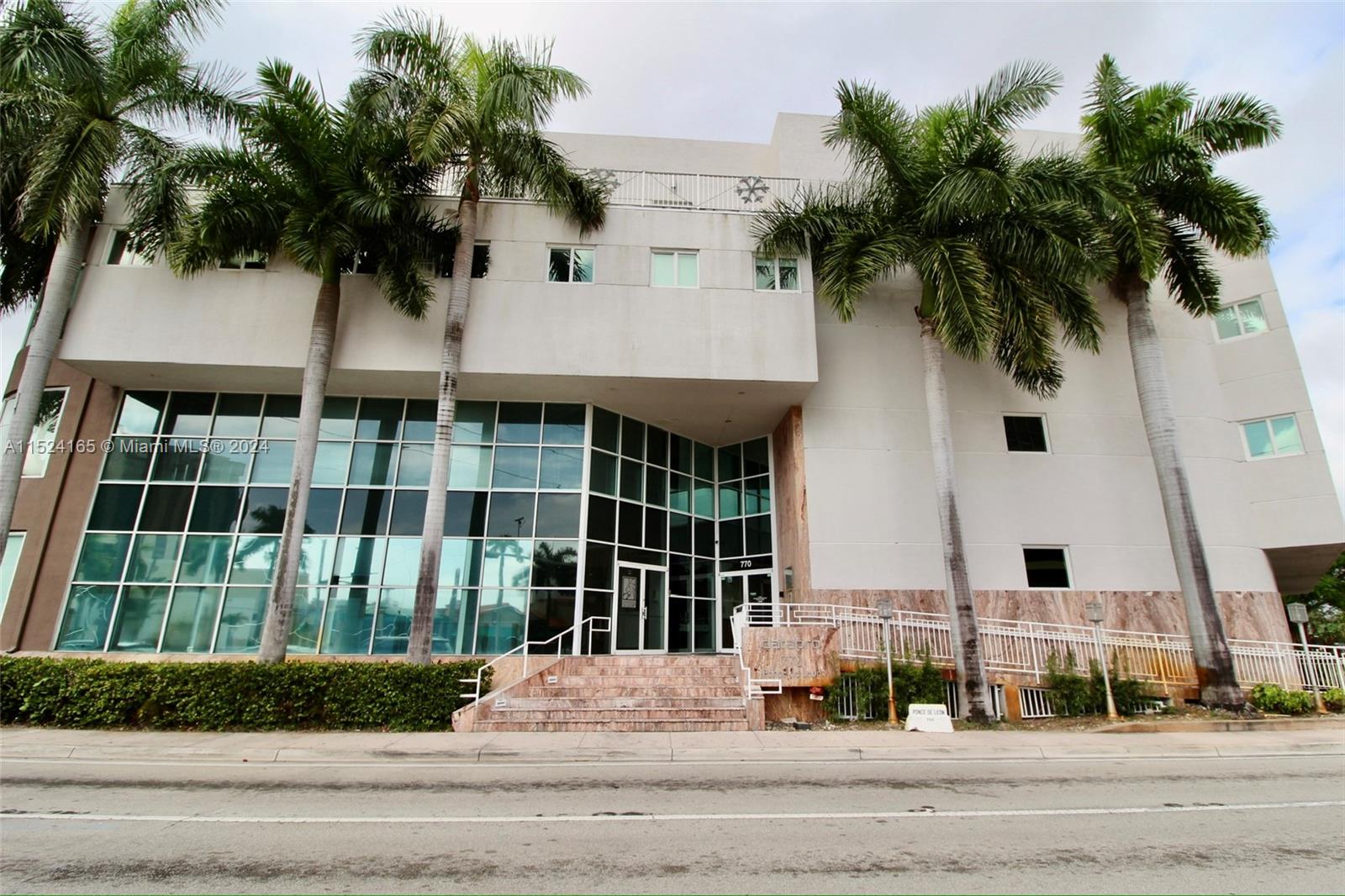
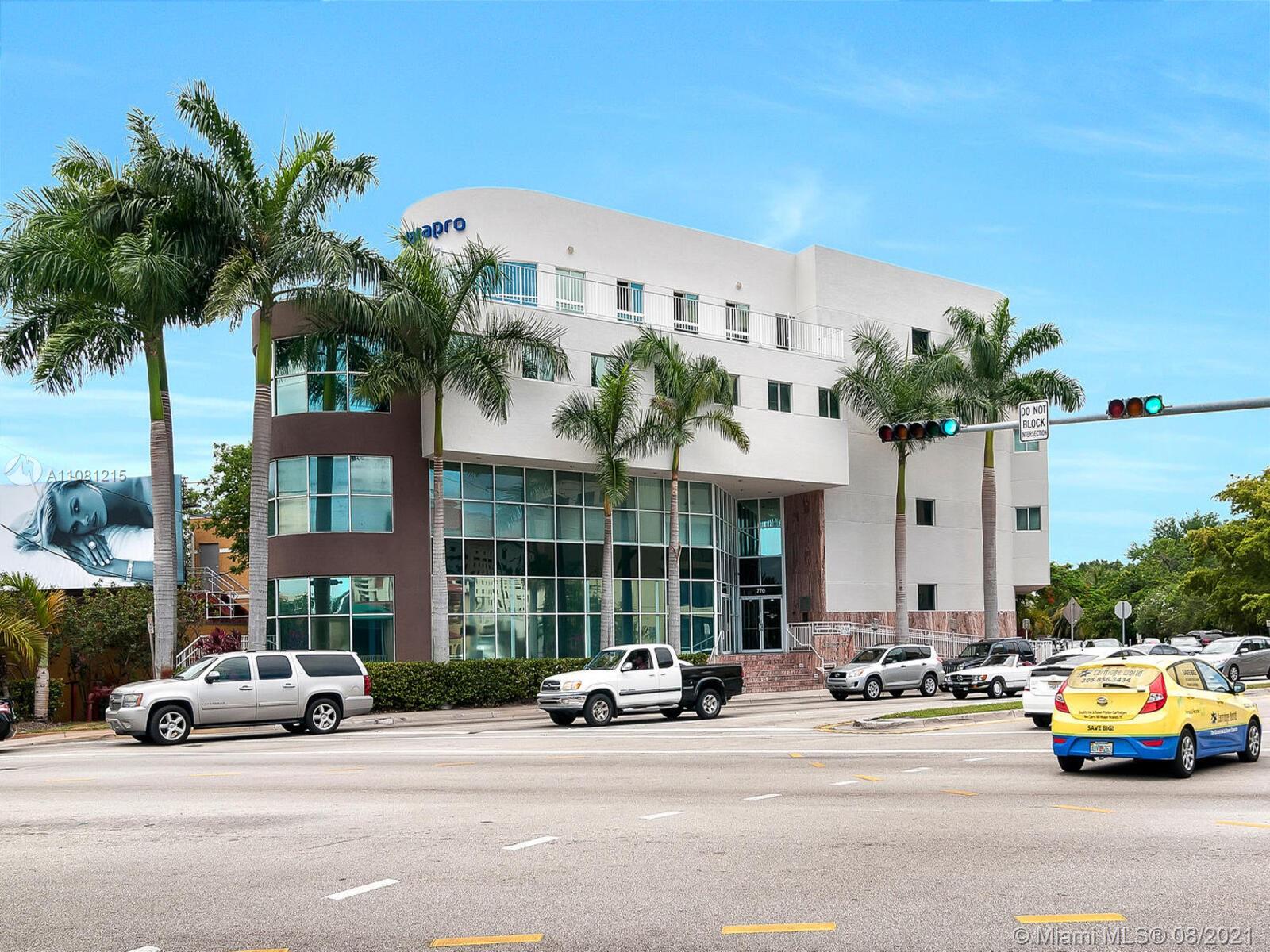
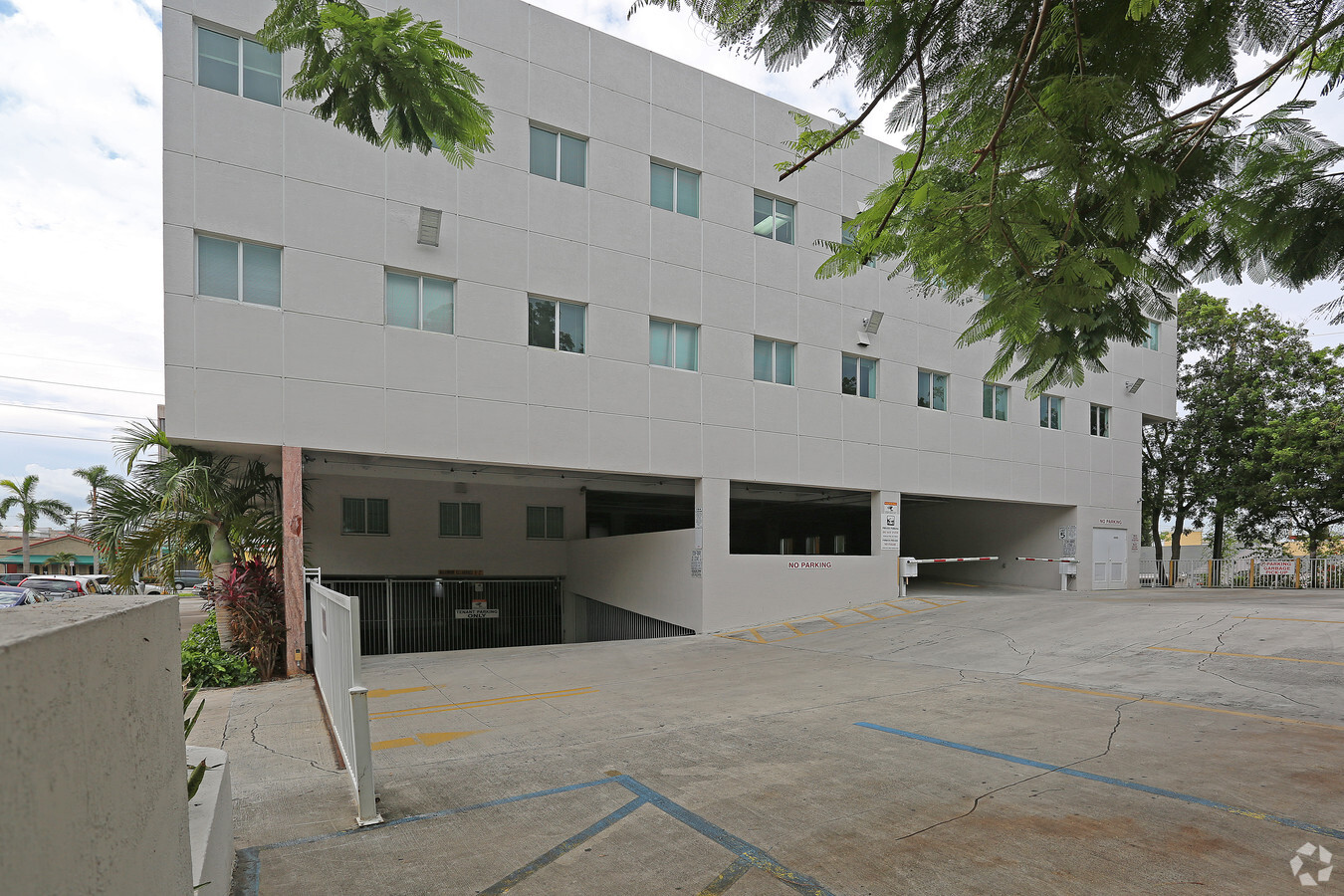
770 Ponce de Leon, Miami-Dade County, Florida, 33134
Size: 9,000 sq. ft.
Price: $29.50 per sq. ft. per annum
770 Ponce de Leon
Building Description
ONE Sotheby's International Realty is proud to present an exceptional leasing opportunity at 770 Ponce De Leon Boulevard, ideally located in the heart of the Coral Gables submarket in Miami-Dade County, Florida. The second floor, comprising 9,000 square feet, is thoughtfully designed to accommodate modern business operations. Among its key features are 22 perimeter offices, two executive offices, a glass- enclosed conference room, and an open bull-pen area. Additionally, the space includes a large training center and a full kitchen, providing both functionality and convenience. Supporting advanced business needs, the building includes a dedicated IT room with two high-speed T-1 lines, ensuring reliable internet access, email, file sharing, and other essential applications. Tenants will also benefit from 40 dedicated parking spaces additionally parking is available in the building and off-street, along with signage rights for enhanced visibility. This upscale, four- story office building spans 60,939 square feet and offers premium office spaces to suit a variety of professional needs. 770 Ponce De Leon presents a rare opportunity in the high barrier- to-entry, infill market of Downtown Coral Gables. Positioned strategically between Interstate 95 and the Palmetto Expressway, with close proximity to the 836 Expressway and Miracle Mile, the property provides seamless connectivity and accessibility for businesses and clients alike. This exceptional location allows tenants to capitalize on the area’s significant rental income growth and value appreciation, driven by Coral Gables’ reputation as one of South Florida’s most desirable commercial submarkets.
Building Highlights
Rate: $29.50 P/SF
• Versatile Workspace: 9,000 Square Feet
• 22 perimeter offices, Two executive offices, Glass-enclosed conference
room, Open bull-pen, Large training center, One full kitchen
• 40 parking spaces
• IT room has 2 dedicated T-1. A T-1 is a high speed data transmission
line. Used by businesses to provide reliable, dedicated T1 service for
internet access as well as other applications including email, file sharing,
web hosting and more.
• Signage rights available
• 2nd floor available with or without furniture
4019 South Le Jeune Road, Miami-Dade County, Florida, 33146
Size: 2,980 sq. ft.
Price: $100 per sq. ft. per annum
Turn Key Coral Gables Restaurant
One Sotheby's International Realty is proud to present an exceptional restaurant space now available for lease at 4019 S LeJeune Rd., in the vibrant city of Coral Gables, FL. This prime 4,850 SF location offers 50 feet of prominent frontage on LeJeune Rd., providing excellent visibility in a high-traffic area. Ideal for restaurateurs looking to establish their presence in one of Coral Gables' most dynamic neighborhoods, this restaurant is move-in ready and perfectly suited for a thriving dining establishment. Don't miss the opportunity to lease in this sought-after location.
Facing SW 42nd Ave., also known as LeJeune Rd., the property has an average of 26,000 vehicles per day (VPD). LeJeune Rd. is one of the city's main arterial corridors connecting various neighborhoods and provides access to many popular destinations within the city and the surrounding areas of Miami-Dade.
Building Highlights
• Situated in Coral Gables, FL, the "City Beautiful," 4019 S LeJeune Road offers an exceptional restaurant space for lease, perfectly designed to attract a steady stream of patrons from the surrounding vibrant mix of residential, retail, and office buildings. This 4,850 SF space boasts 50 feet of prominent frontage on LeJeune Road, providing excellent visibility and accessibility for both drive-by and pedestrian traffic. Located just minutes from Merrick Manor, a premier luxury development featuring upscale residences and boutique shops, this property is ideally positioned to benefit from the area’s affluent customer base, making it a prime location for a successful dining establishment.
The interior layout is ideal for a bustling dining establishment, featuring spacious dining areas, and ample kitchen space to accommodate a variety of culinary concepts. Located in a highly dense residential area with affluent neighborhoods just across Bird Road, the restaurant benefits from a built-in customer base eager for local dining options. This prime location presents an outstanding opportunity for restaurateurs to lease a property that combines strategic positioning, aesthetic appeal, and a strong foundation for growth in one of Coral Gables' most desirable commercial and residential districts.
• 4019 S LeJeune Road benefits from numerous public transportation systems running directly through and in close proximity to the property. The MetroBus system has two separate directional routes, North-South and East-West, both crossing in front of the property, as well as the Miami Dade Metrorail station just half a mile away.
• - 50' frontage on LeJeune Rd.
- Very Walkable (85 Walk Score)
- Multiple options for public transportation
- Centered between commercial and residential areas
- Property is centrally located near the Miami International
Airport, Coconut Grove, Brickell, Downtown and Wynwood.
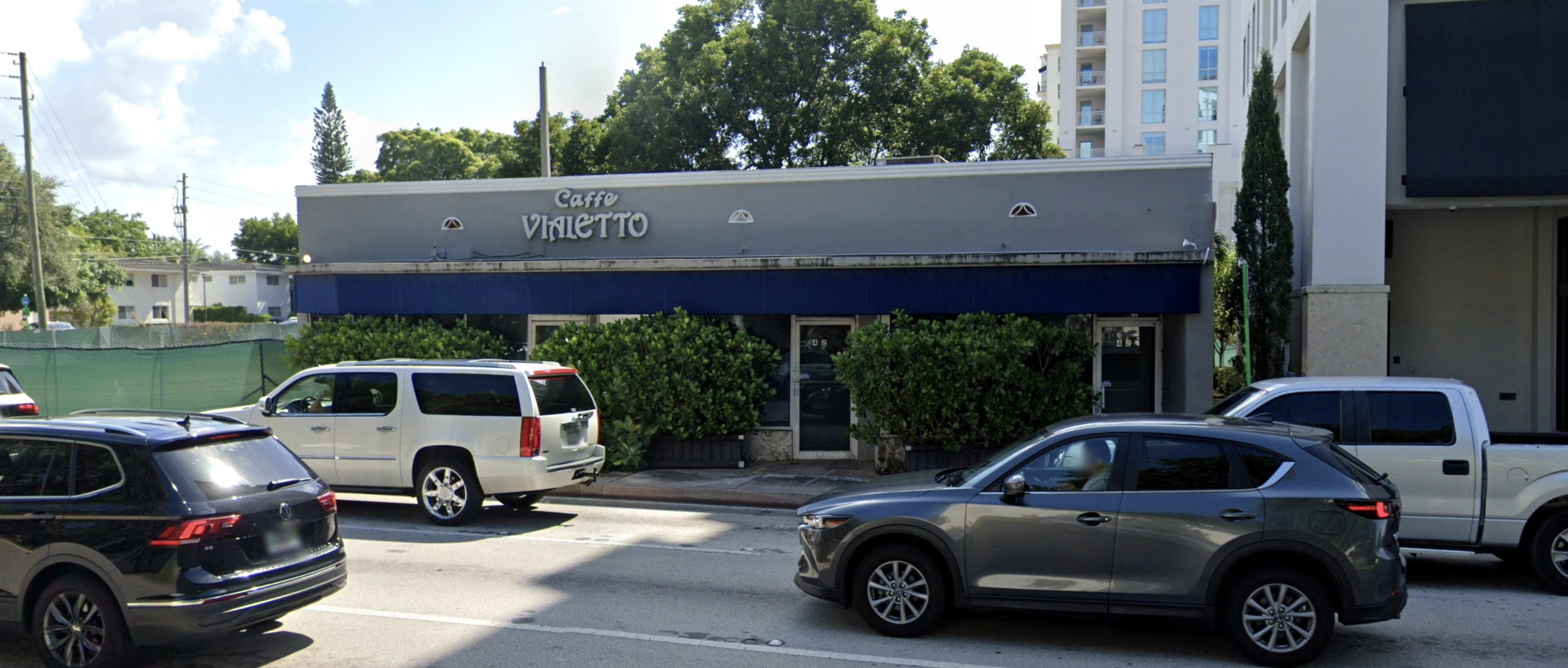
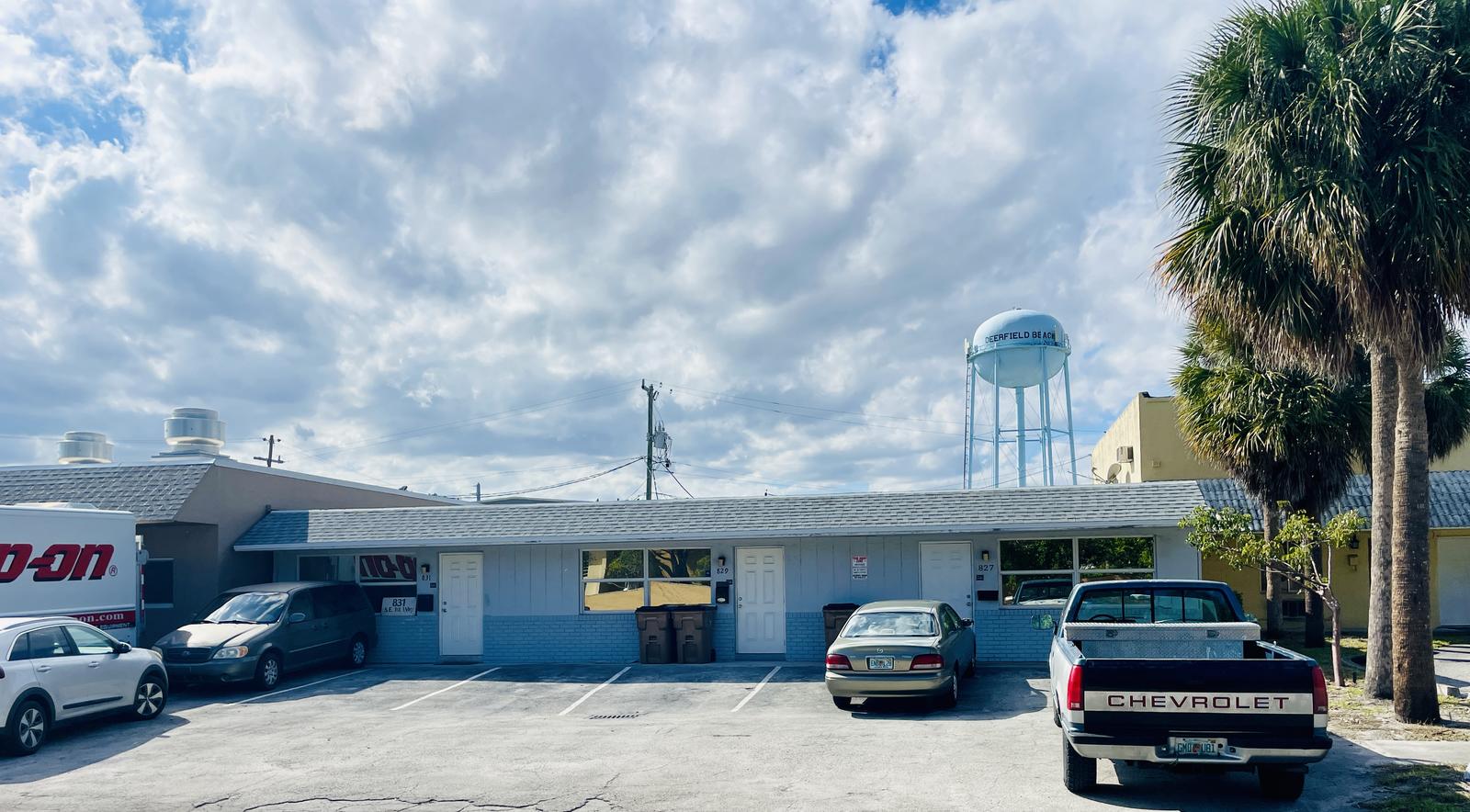
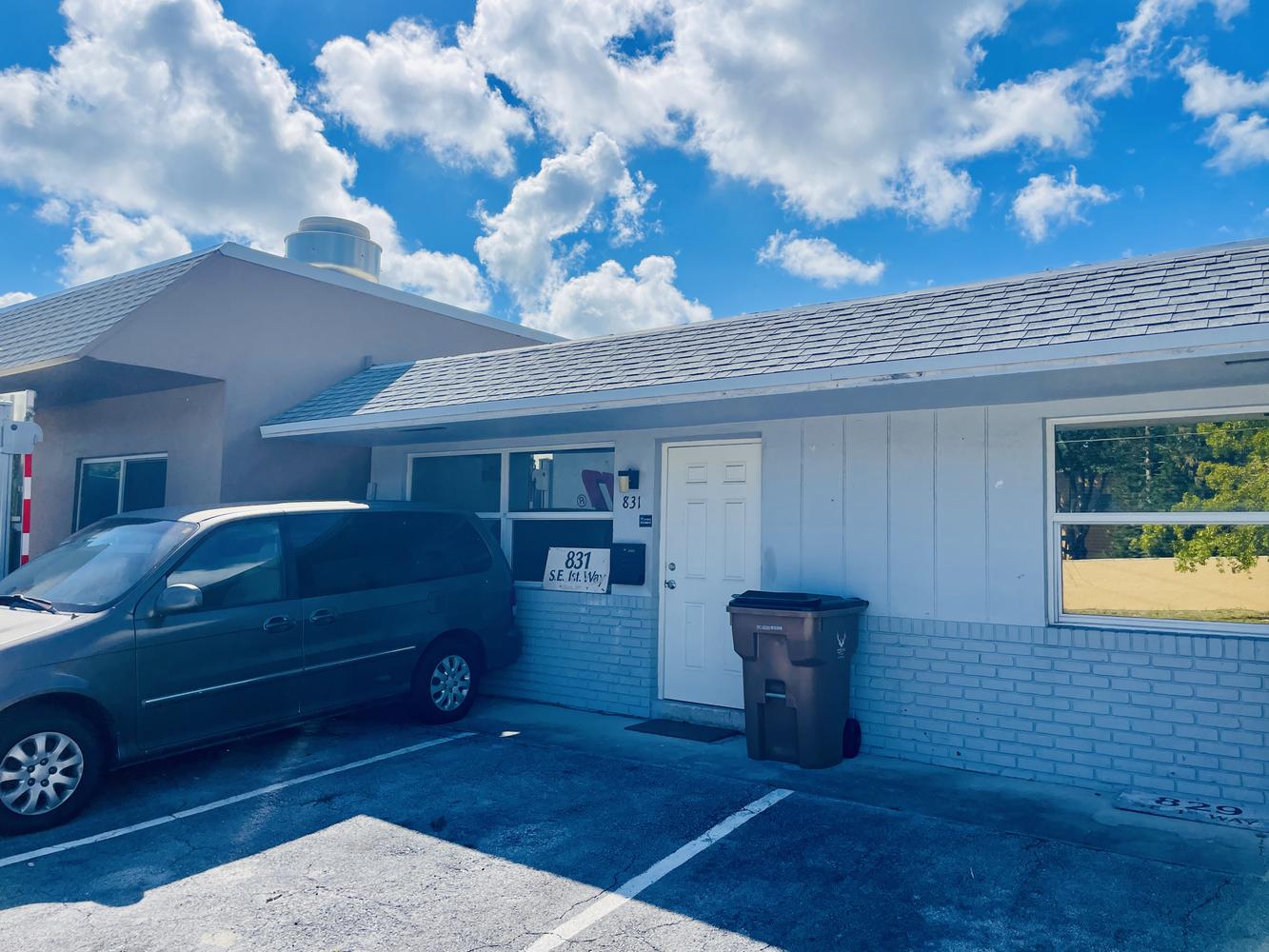
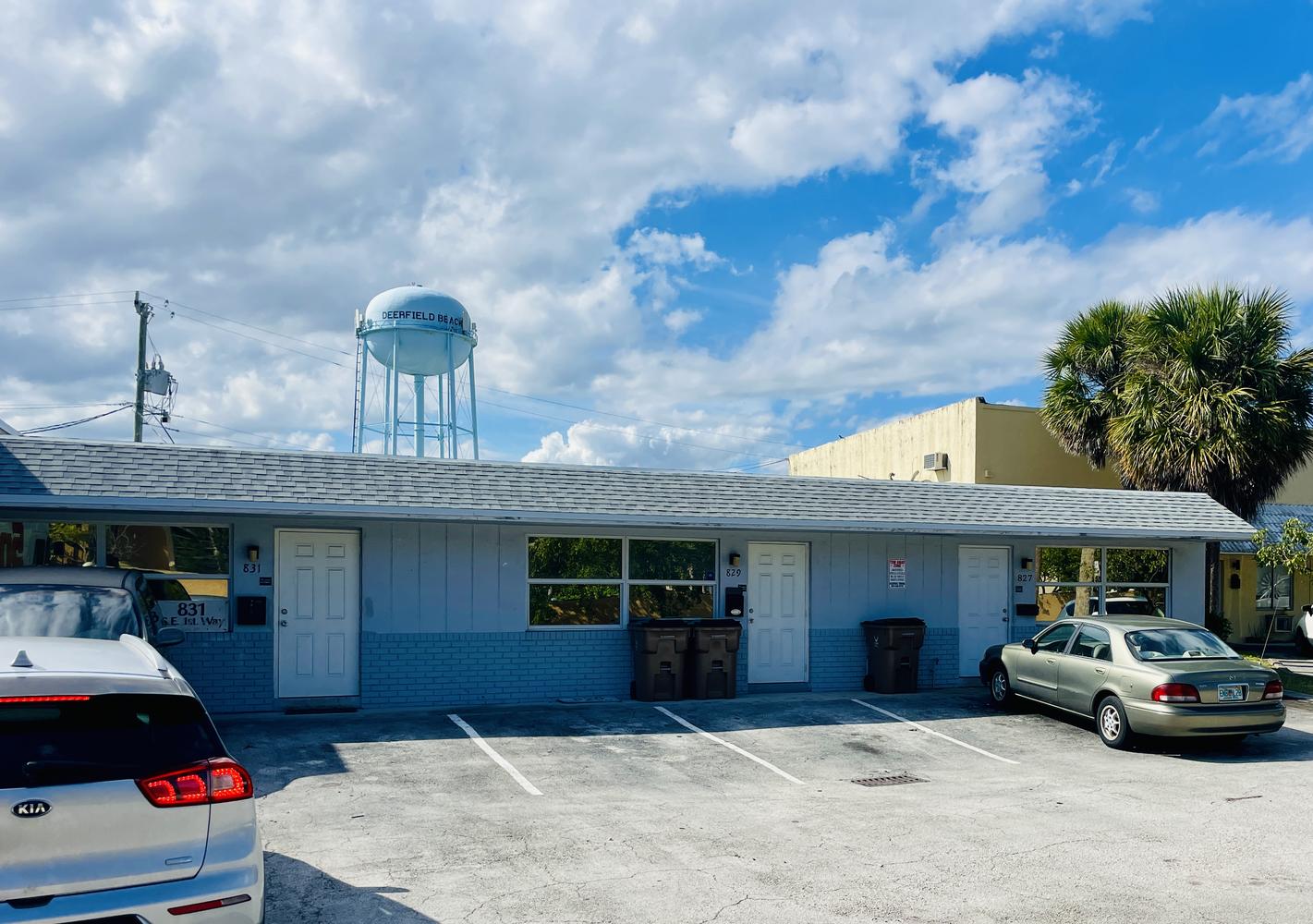
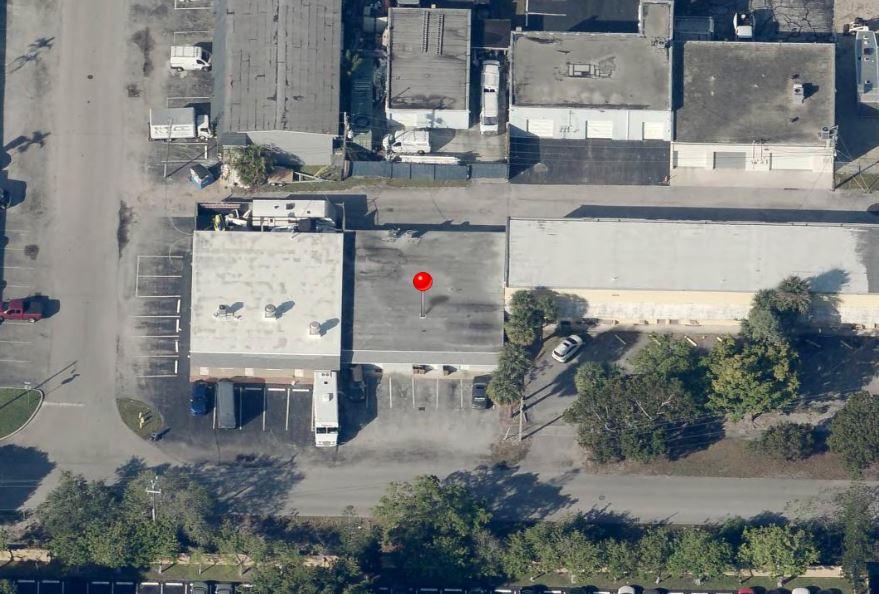
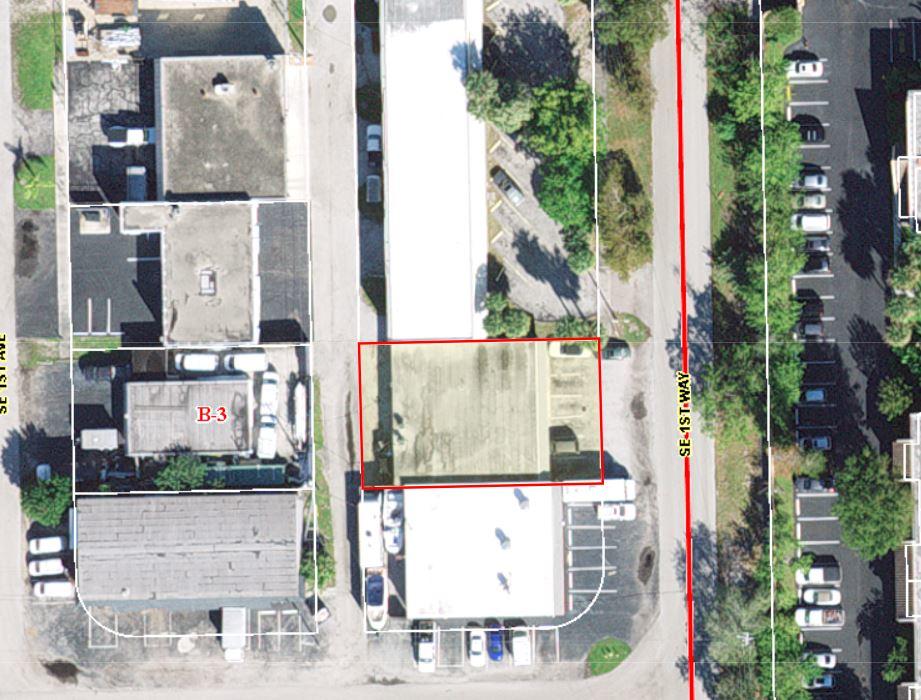
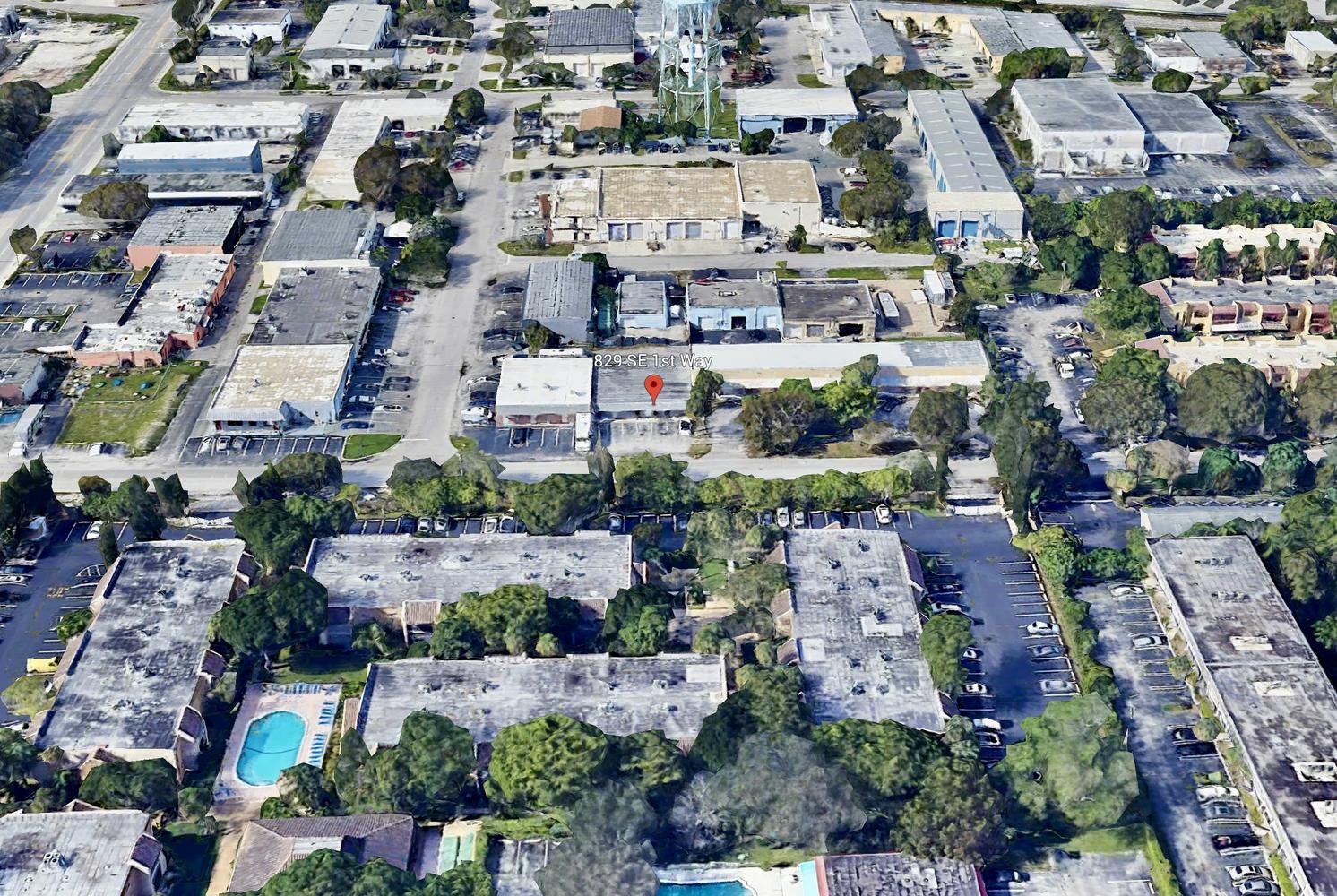
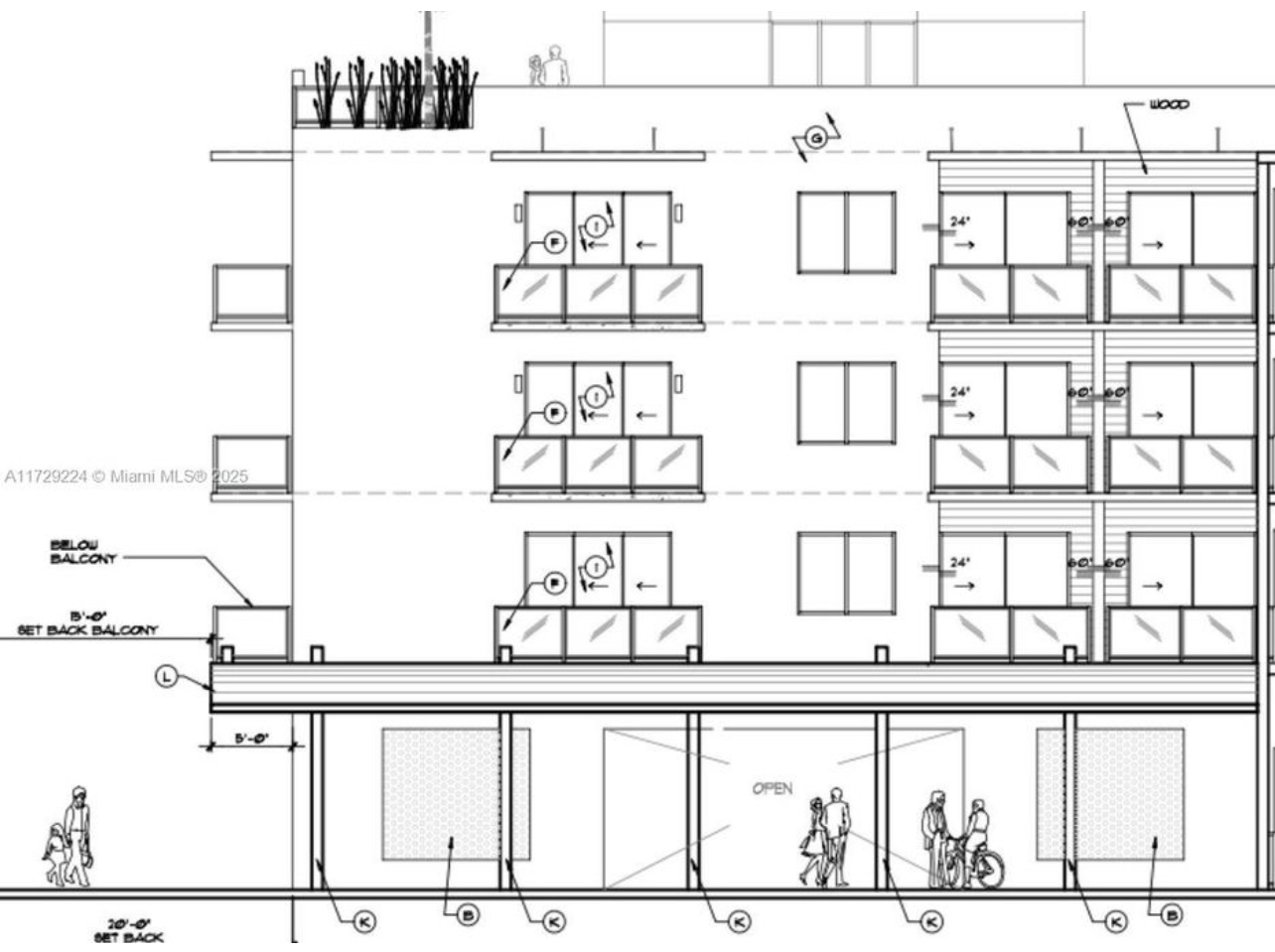
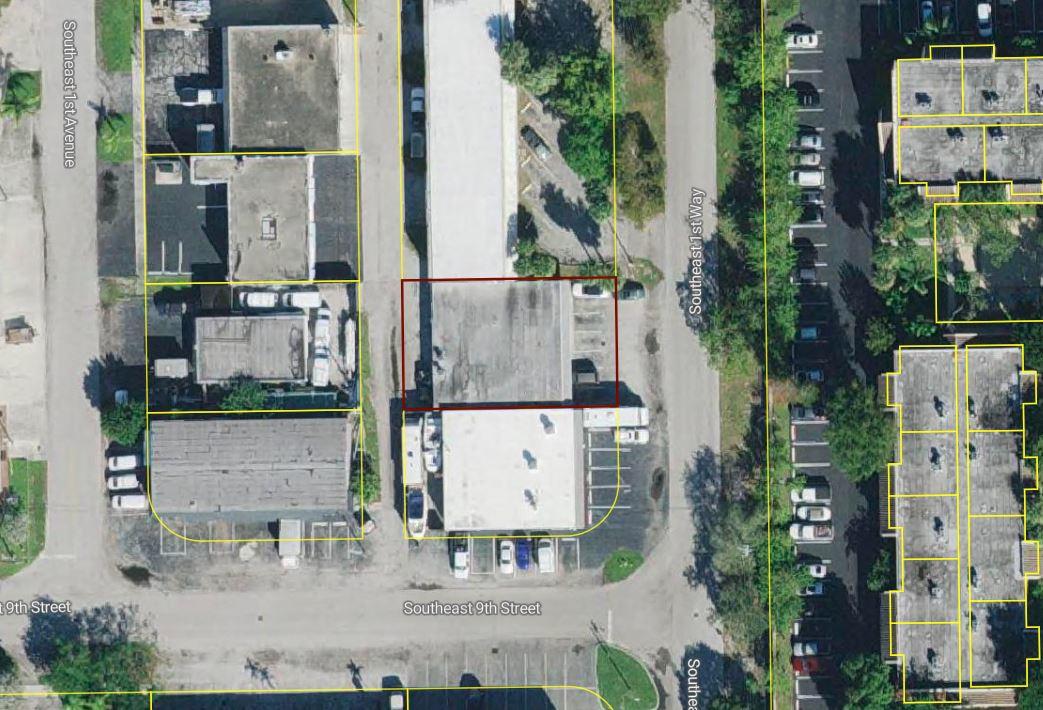
827 Southeast 1st Way, Broward County, Florida, 33441
Size: 1,226 sq. ft.
Price: $2,000 fixed price per month
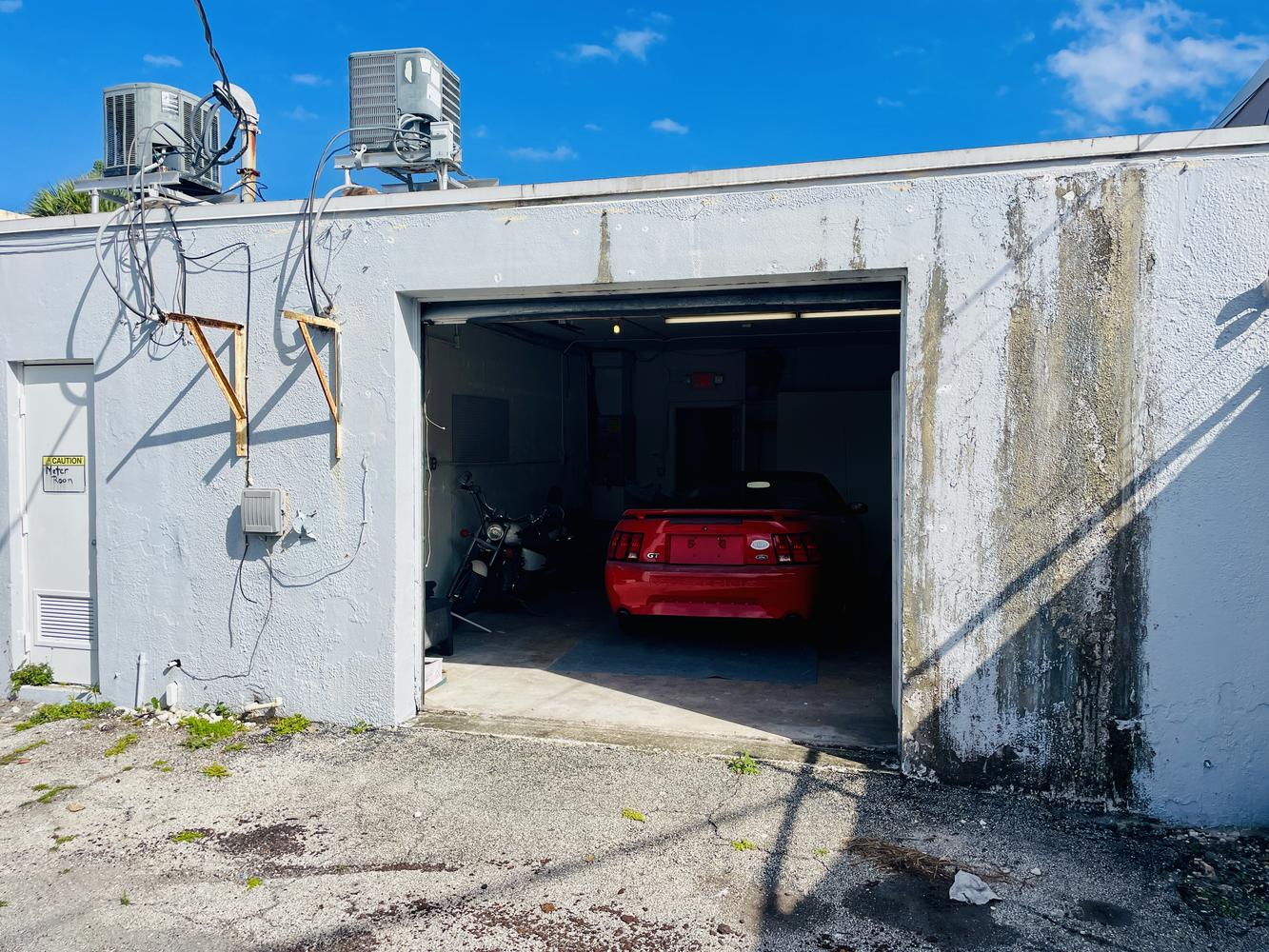
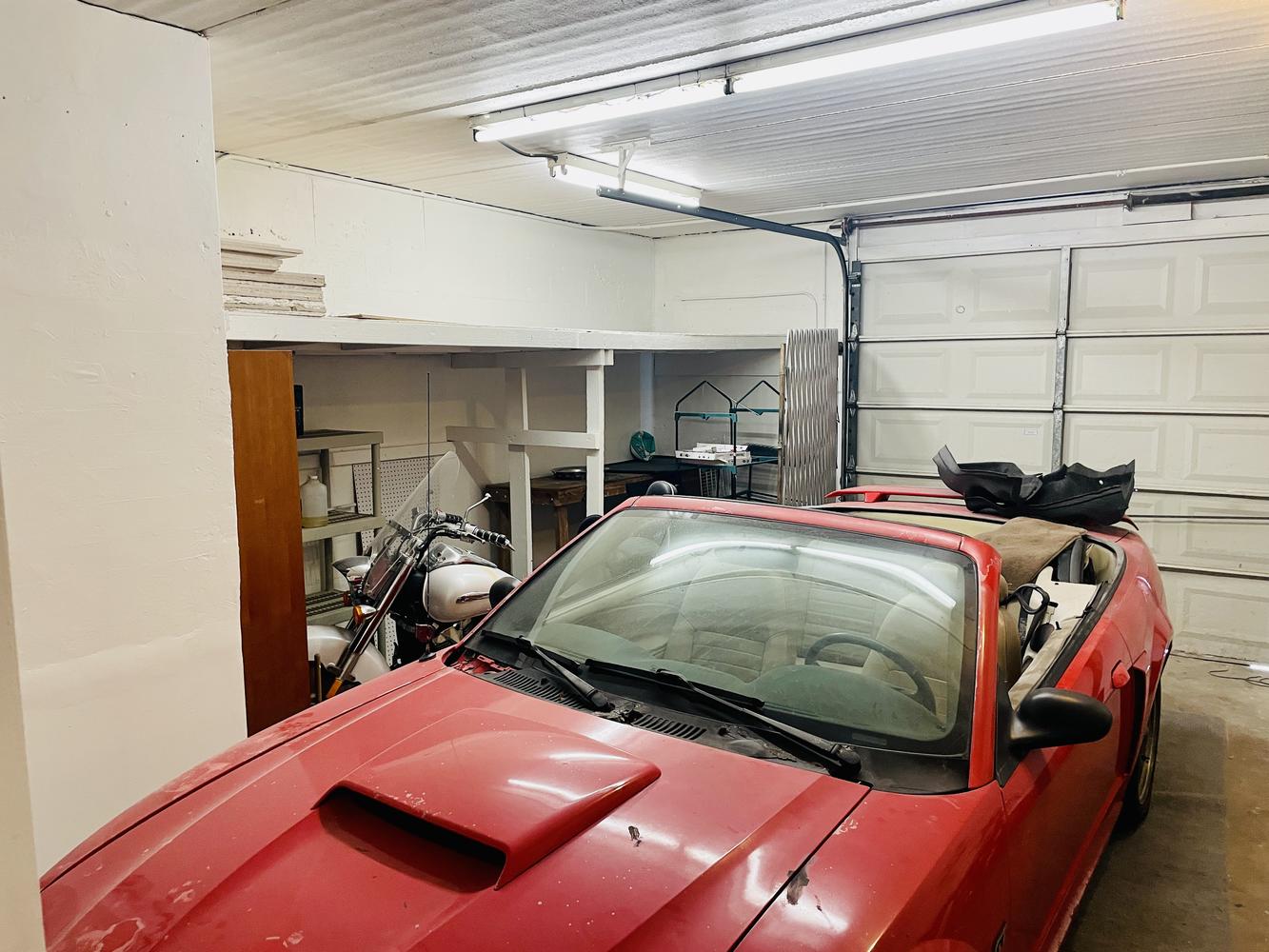
Small Bay Warehouse for Lease
Rare small bay warehouse for lease. Approximately 1,226 sq. ft. available for lease. This well located warehouse building centrally located in Deerfield Beach. This newly remodeled space include, customer waiting area 1 grade level door, 12’ ceiling heights. Desirable B3 zoning would permit storage, trade shops, metal work, woodworking, plumbing, roofing, electrical and associated building trades, contractors office, light manufacturing, and warehouse/ distribution.

2100 East Sample Road, Broward County, Florida, 33064
Size: 1,330 sq. ft.
Price: $429,000
Remodeled Medical Office Condo
Completely remodeled medical office condo for sale in prestigious Lighthouse Point. This condo includes large waiting and reception area with ample parking less than 2 miles from Broward Health North. This suite contains 3 private offices and conference room. Recent upgrades include new flooring, lighting, painting and ADA bathroom. Located in an area of high-income demographics

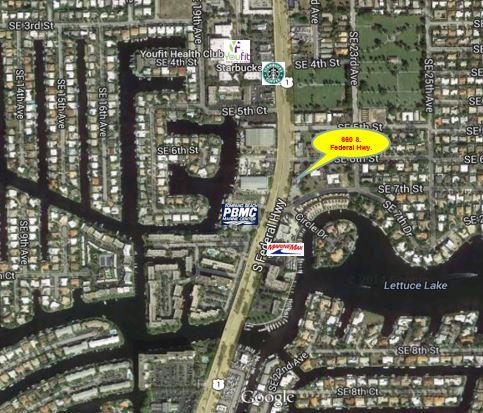
660 South Federal Highway, Broward County, Florida, 33062
Size: 1,250 sq. ft.
Price: $1,500 fixed price per month
Prominent Federal Hwy Office Space
Lowest priced office space on Federal Hwy!! Two suites available approximately 1,250 Sq. Ft. +- Interior recently remodeled for general office. Prominent features include 3-4 offices, private bathrooms and ample parking.

Omaha, Nebraska, 68144
Size: 400,000 sq. ft.
Price: $7,500,000
Cap 10%+ Trophy Mall
The Mall is a prime investment and leasing opportunity focused on upscale retail, entertainment, and lifestyle experiences. With recent new tenant commitments, the property is experiencing increased leasing momentum, making it an ideal time for retailers, entertainment venues, and experiential brands to secure space. Positioned in a high-income trade area, The Mall is set to become a revitalized shopping, dining, and entertainment hub.
Key Highlights
Strong Demographics: High-income households & strong consumer spending.
Retail & Entertainment Destination: Ideal for fashion, dining, fitness, and luxury brands.
Leasing Momentum: New tenant signings increasing demand.
Experience-Driven Strategy: Focus on entertainment, fitness, and unique retail concepts.
Proximity to Major Employers: High daily foot traffic potential.
📊 Market Overview & Demographics
Affluent Consumer Base: High disposable income and brand-conscious shoppers.
Lifestyle & Experience Demand: Growing preference for entertainment-driven retail.
Health & Wellness Trend: Increasing demand for boutique fitness, medical offices, and wellness services.
Dining & Social Venues: Consumers seeking high-quality restaurants and nightlife options.

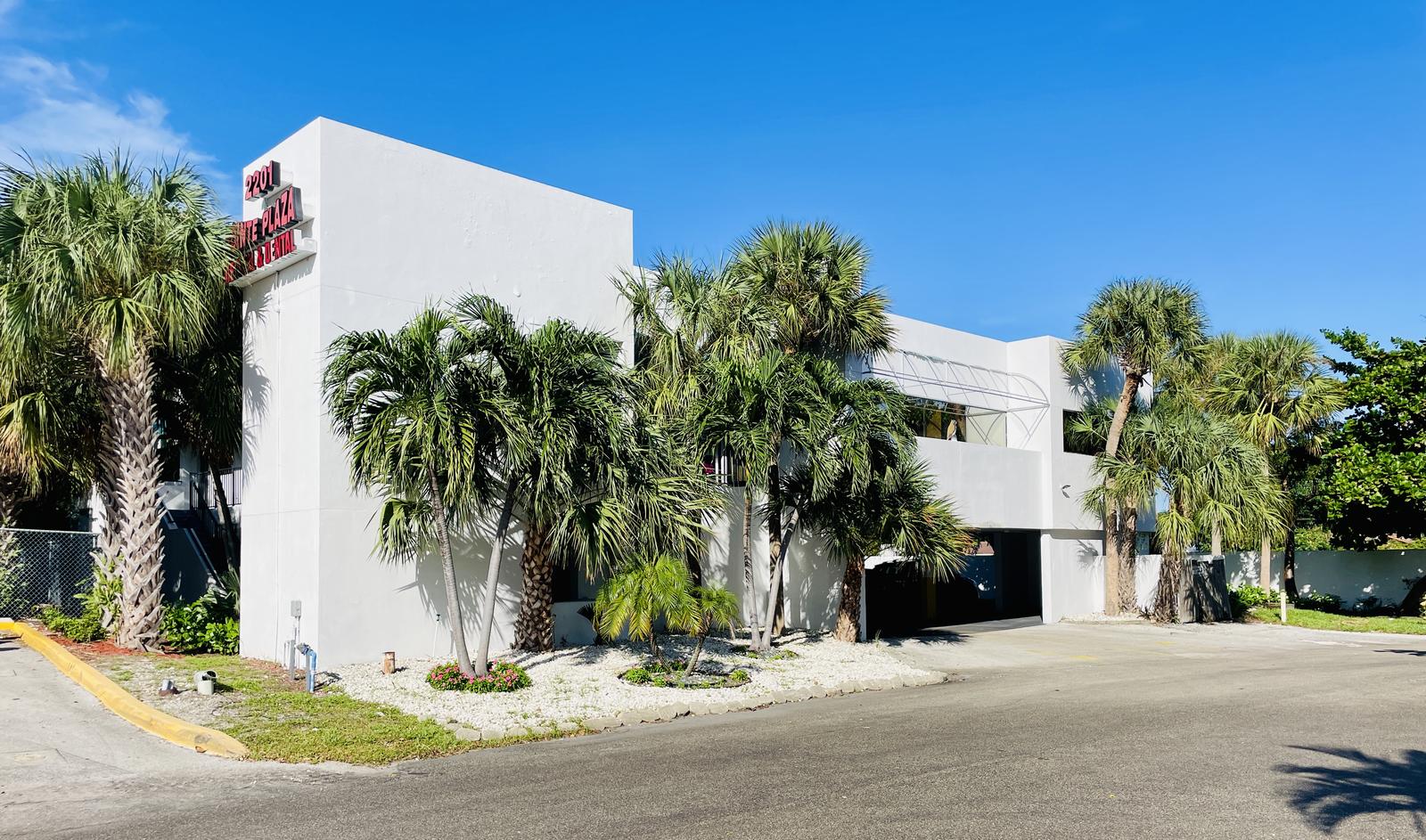
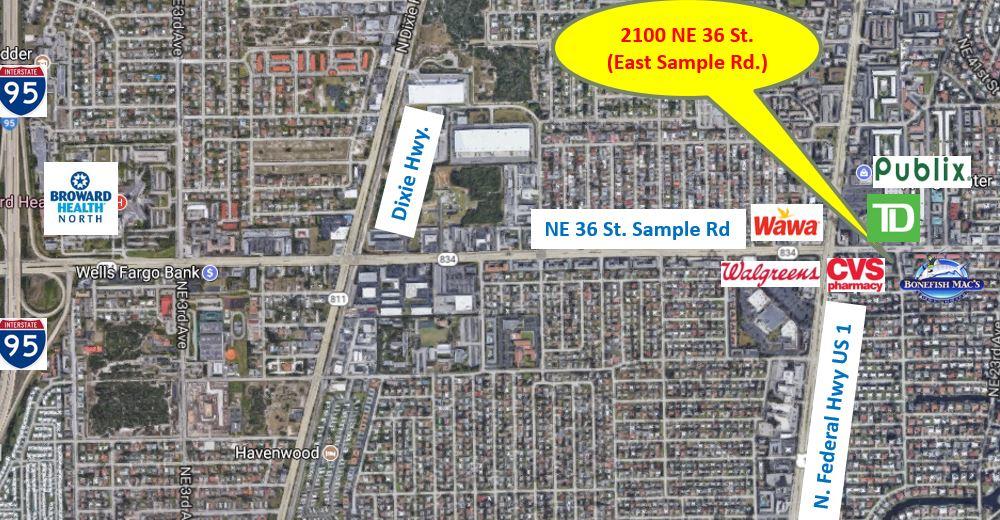
2201 Northeast 52nd Street, Broward County, Florida, 33064
Size: 4,000 sq. ft.
Price: $21 per sq. ft. per annum
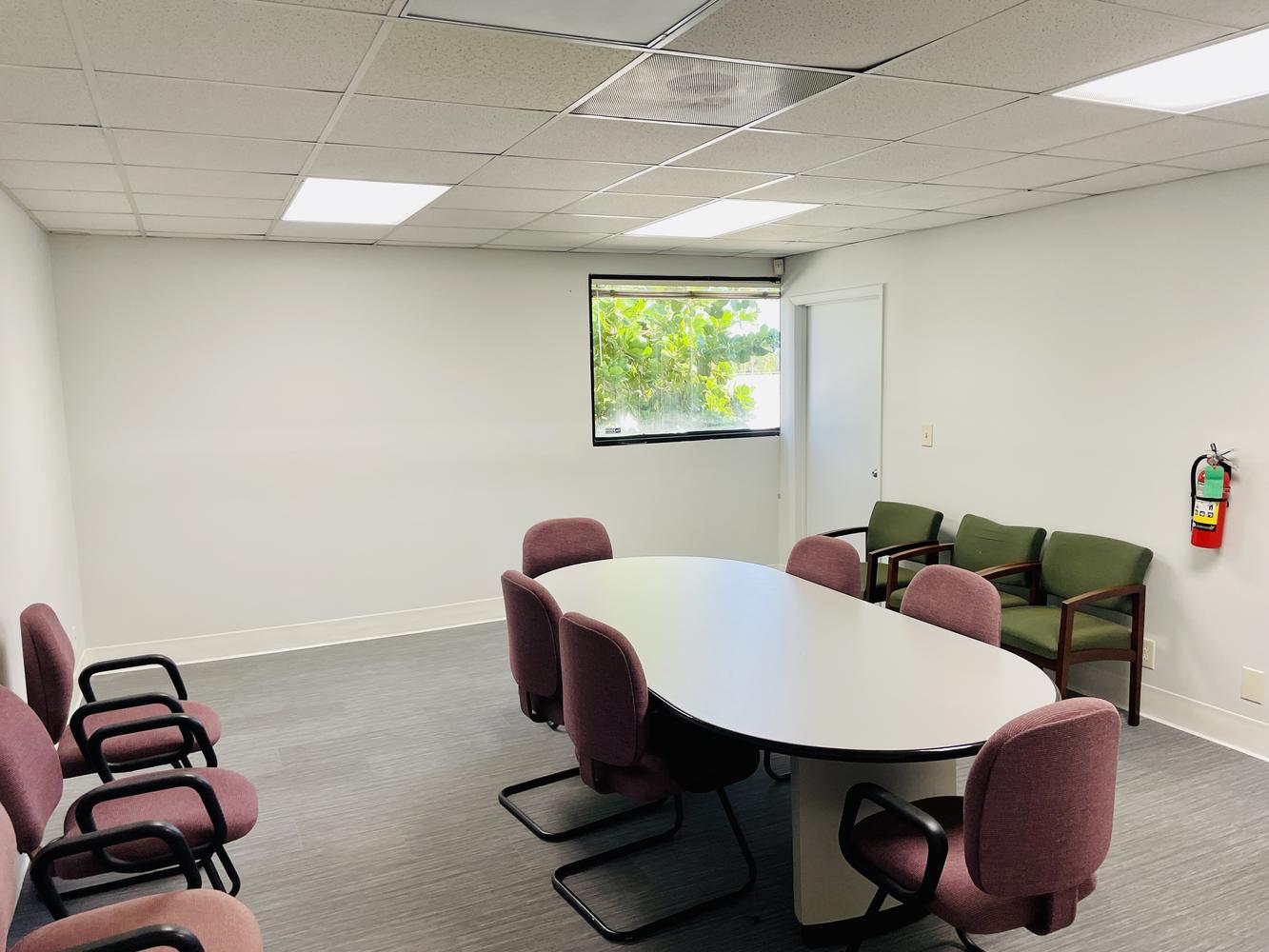
Medical Office Space for Lease
Updated medical office space for lease in prestigious Lighthouse Point. This space includes large waiting and reception area, 6 exam rooms 2 executive offices with shower, lab room and kitchen area with ample covered parking. Located just blocks from the new Broward Health Emergency Center. B3-A Zoning would permit several other office uses including financial services, architectural and construction, and sales and marketing. Located in an area of high-income demographics.

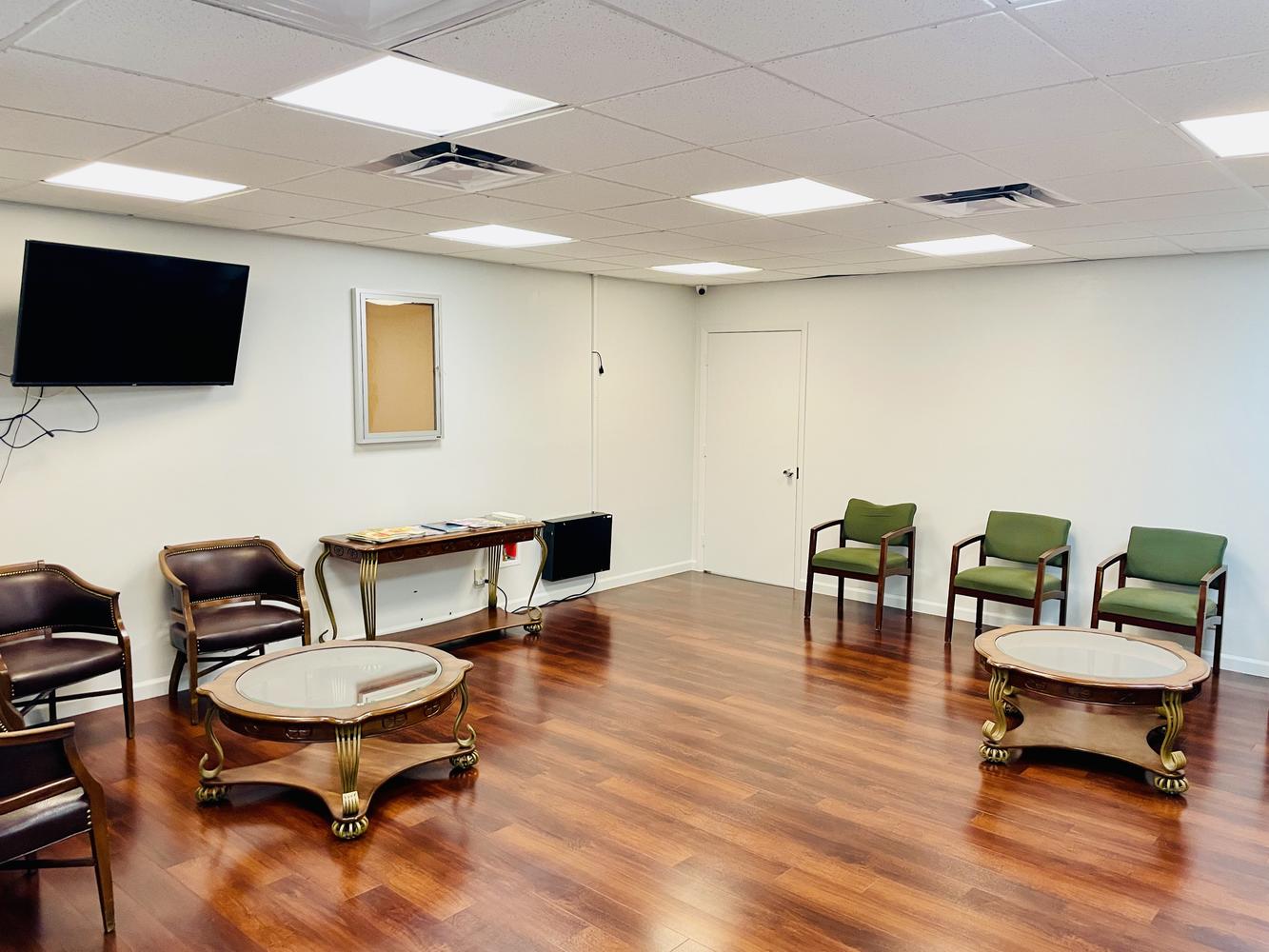
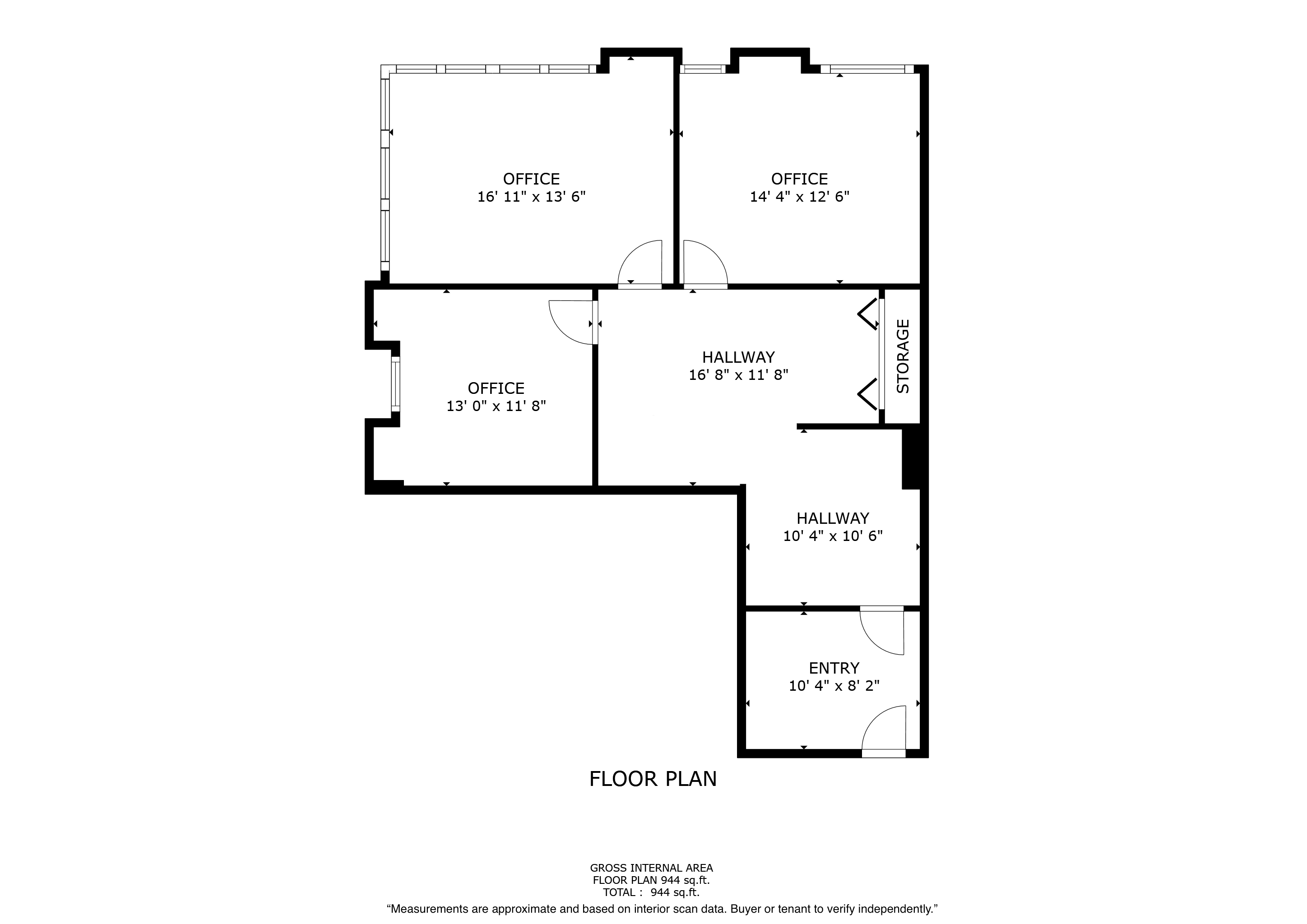
Miami-Dade County, Florida, 33131
Size: 944 sq. ft.
Price: $750,000
Brickell Office Space for Sale
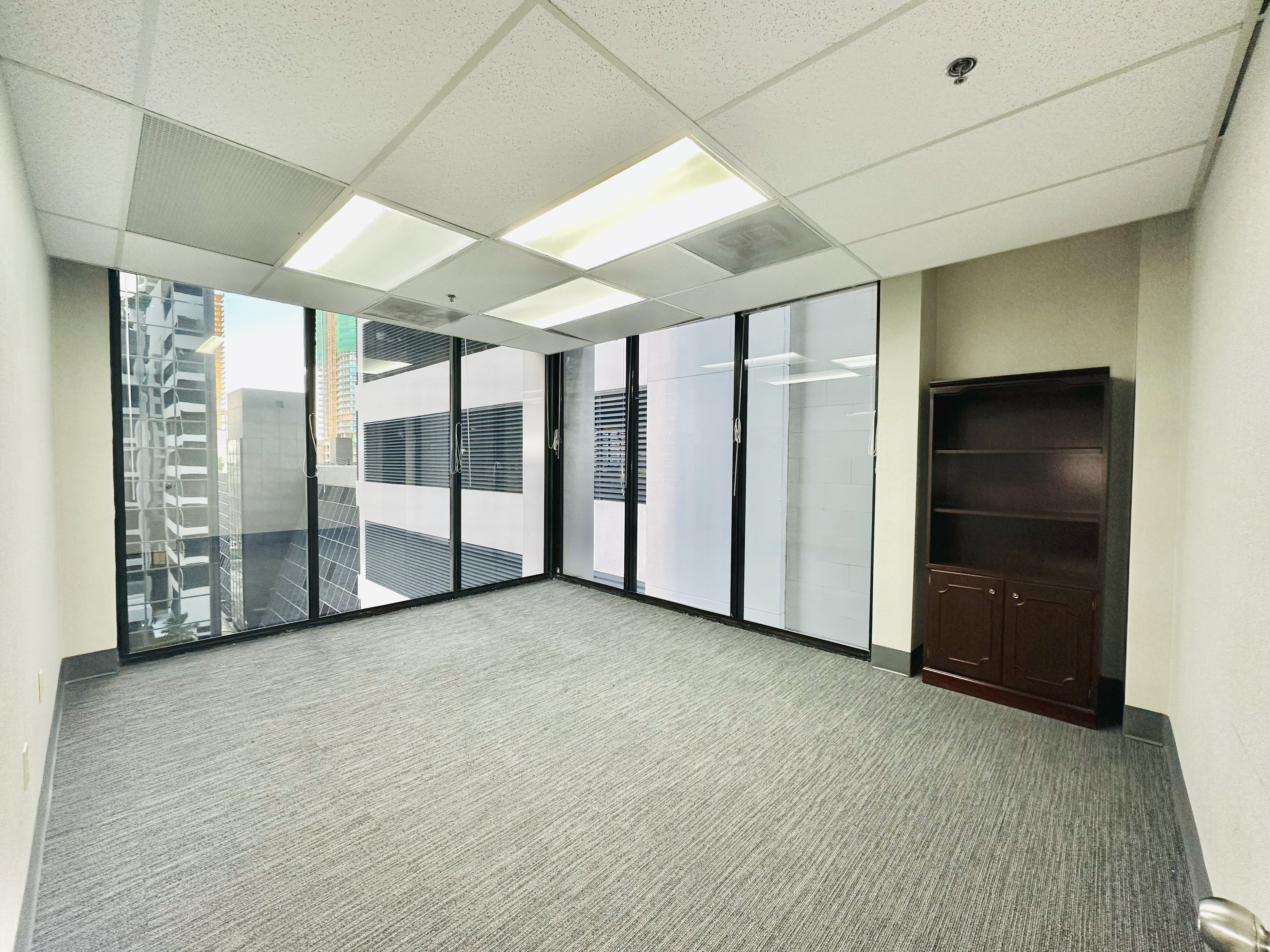
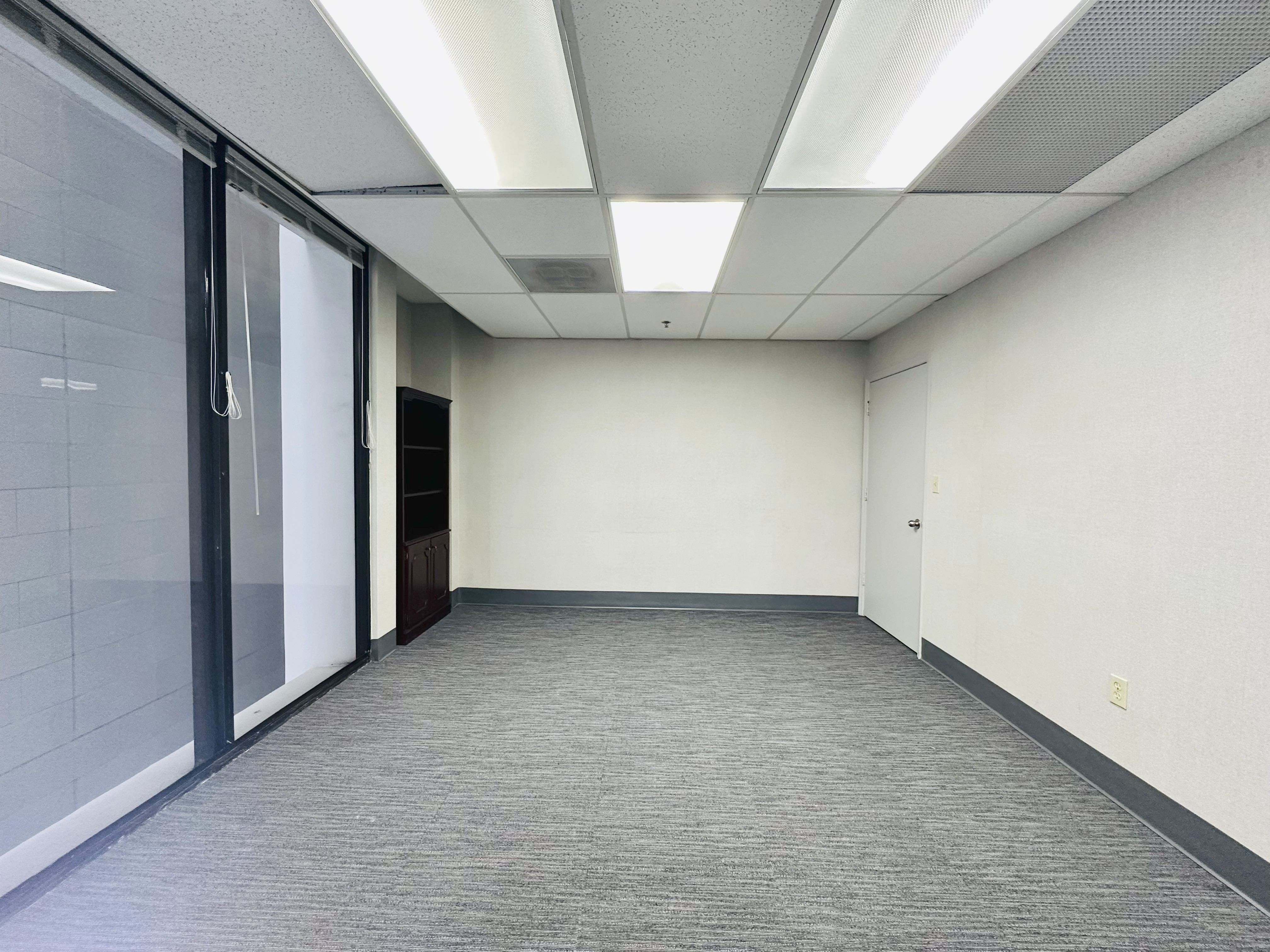
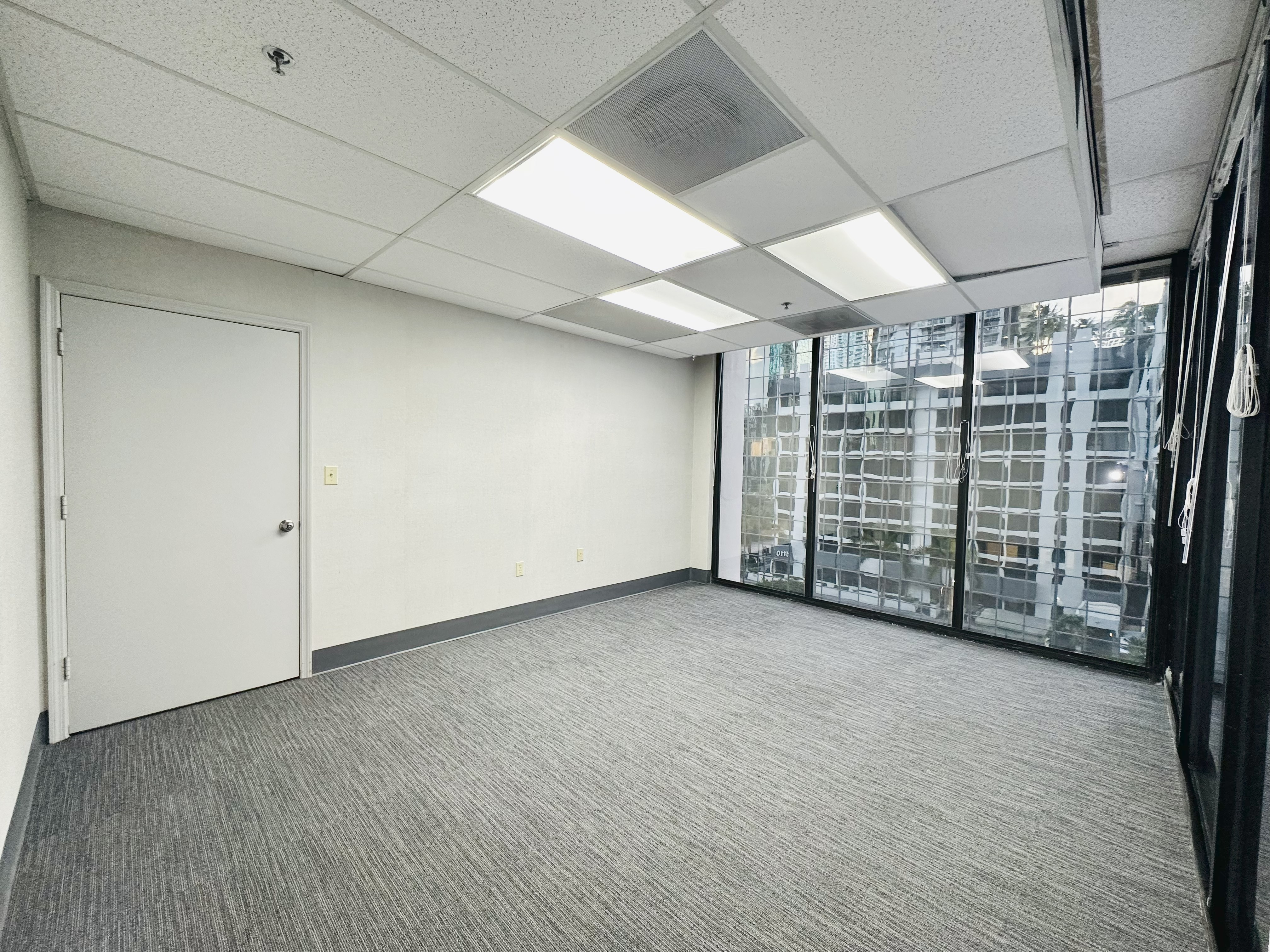
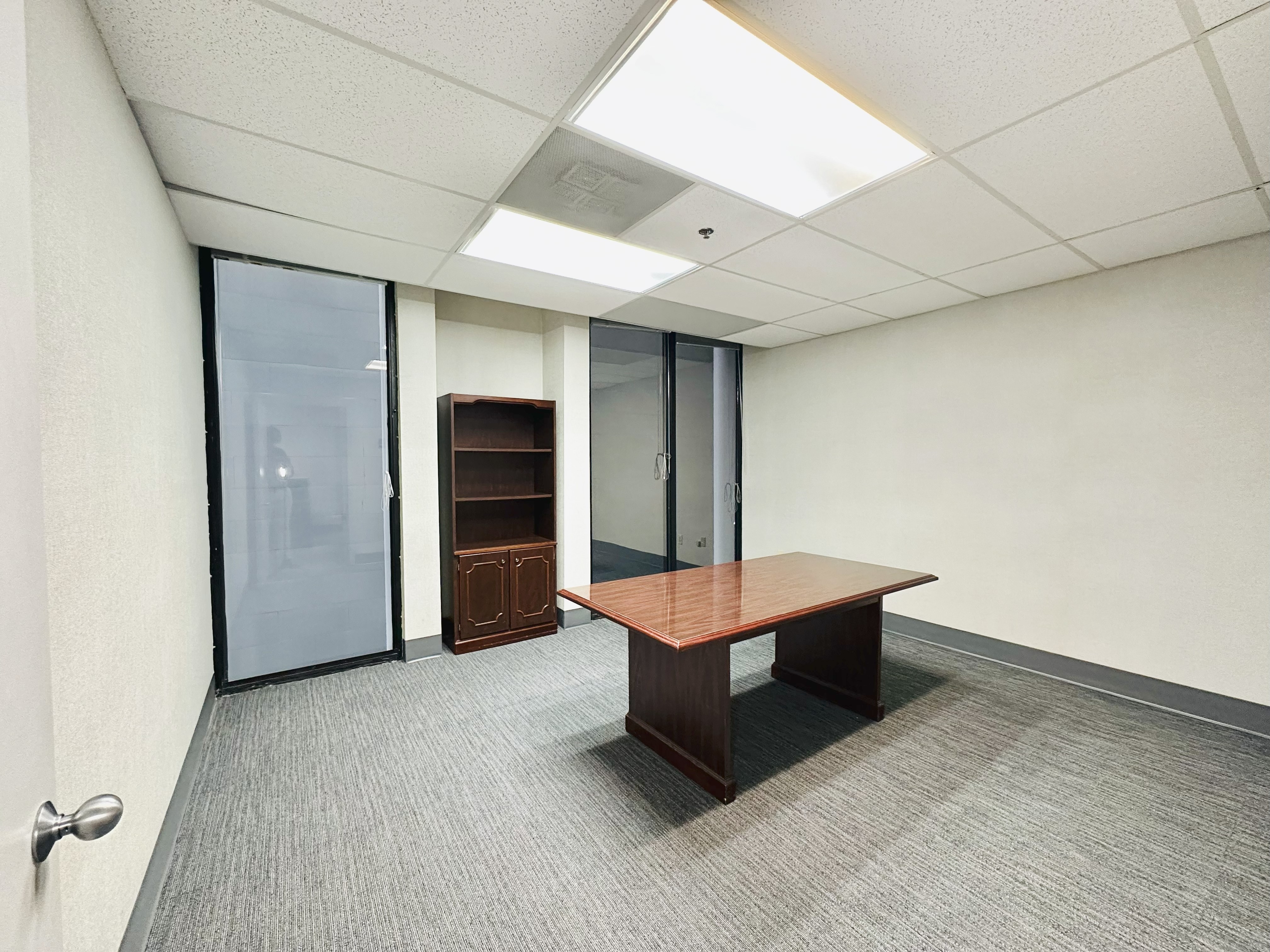
Prime office space in the heart of Brickell Business District! This stunning commercial office suite spans 885 usuable square feet. Positioned on a corner, the office is filled with natural light through out large windows in three separate rooms, creating a bright and welcoming environment. The space features a spacious reception area, ample space for files & supplies. Parking is available at $227.64 per-month per vehicle, unit has access to 2 parking spaces. Easy access to major roads, Metro Rail, Metro Mover, High-end Residential condos and hotels nearby. Enjoy Brickell's vibrant dining, shopping, and business hubs just steps away, in an ideal location to elevate your business presence. Tenant occupied until October 2027 $47 P.S.F. Rental Rate. Investors only. New carpet installed.
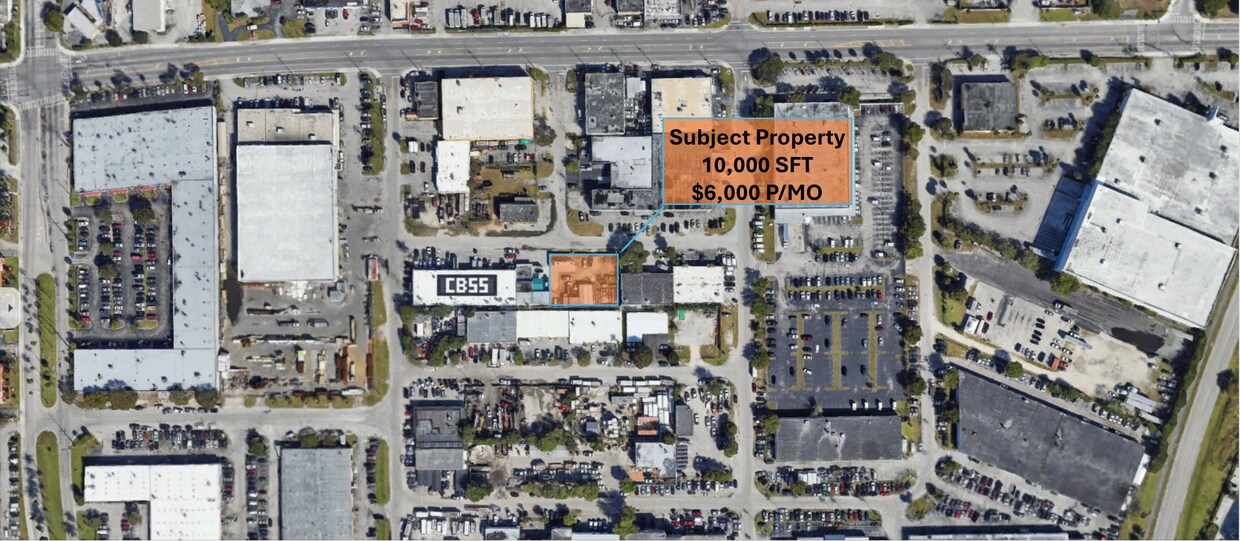
10440 Southwest 186th Terrace, Miami-Dade County, Florida, 33157
Size: 11,100 sq. ft.
Price: $6,000 fixed price per month
Cutler Bay Truck Parking
Building Description
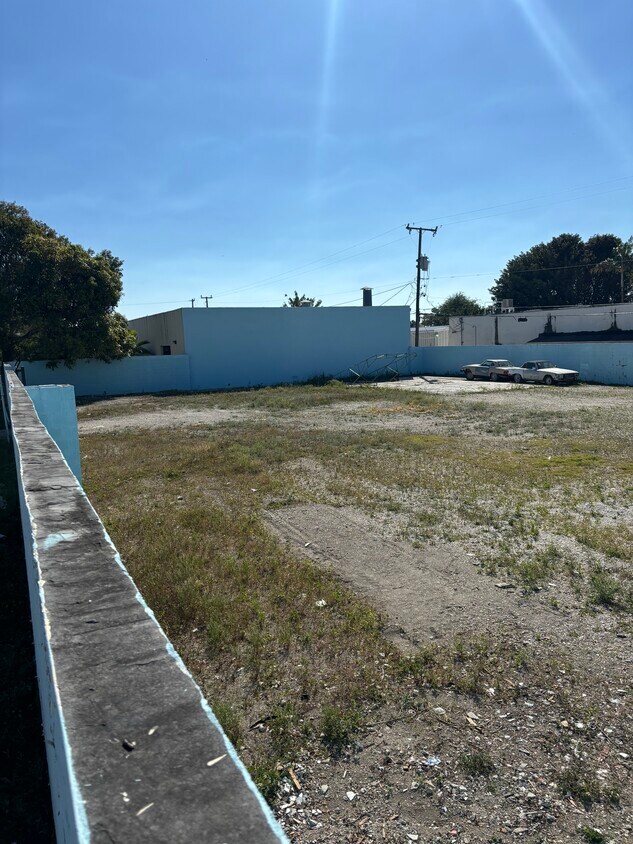
Fenced Industrial Lot for Lease – Prime Multi-Use Opportunity! One Sotheby’s International Realty is pleased to present a walled off 10,000 SF industrial lot available for lease in Cutler Bay, FL, offering an excellent opportunity for businesses seeking a flexible and well-located space for various industrial applications. Whether you need a site for storage, tow yard operations, equipment staging, fleet parking, or other industrial uses, this lot provides the space, security, and accessibility required to support your business needs. Conveniently situated at 10440 SW 186th Terrace, Cutler Bay, FL 33157, this property is located in a well-established industrial and commercial district, surrounded by warehouses, manufacturing facilities, and office parks, making it an ideal location for businesses that require proximity to key suppliers, distributors, and service providers. One of its strongest advantages is its prime accessibility, being just half a mile from Florida’s Turnpike, which ensures seamless connectivity to major transportation routes, facilitating efficient logistics and distribution operations. The fully fenced perimeter enhances security and privacy, making it an excellent choice for businesses that require a safe and controlled environment for their assets, equipment, or fleet. The lot’s industrial zoning allows for a wide range of uses, making it an adaptable solution for businesses looking to expand or establish a strategic base in a high-demand commercial and industrial corridor. With ample space, convenient access, and a strong location in an area known for industrial activity, this property presents a rare leasing opportunity for companies looking to optimize their operational efficiency. Secure a strategically located industrial lot that offers both convenience and versatility.
Building Highlights
Rate: $6,000 P/MO
SFT: 10,000
Tow Truck Operators: A fenced Industrial lot provides a secure storage area for towed vehicles
Equipment Rental Companies: Store heavy equipment, machinery, and tools in a secure and easily accessible location
Construction Companies: Use the lot for equipment and material storage, or as a staging area for projects
Landscaping and Lawn Care Services: Store equipment, trucks, and materials in a secure and organized manner
Trucking and Transportation Companies: Park and store trucks, trailers, and equipment
Scrap Metal Recycling: Collect, process, and store scrap metal
Car and Truck Sales: Store inventory for car and truck dealerships
Equipment Maintenance and Repair: Use the lot as a repair and maintenance facility for heavy equipment and machinery
Disaster Response and Recovery: Store equipment and supplies for disaster response and recovery efforts
Environmental Remediation: Store equipment and supplies for environmental cleanup and remediation cleanups
Agricultural Services: Store equipment, supplies, and materials for agricultural businesses
Waste Management: Store waste collection equipment and supplies
Manufacturing and Fabrication: Use the lot for outdoor manufacturing, assembly, or fabrication processes
Government Agencies: Store equipment, supplies, and vehicle's for government agencies
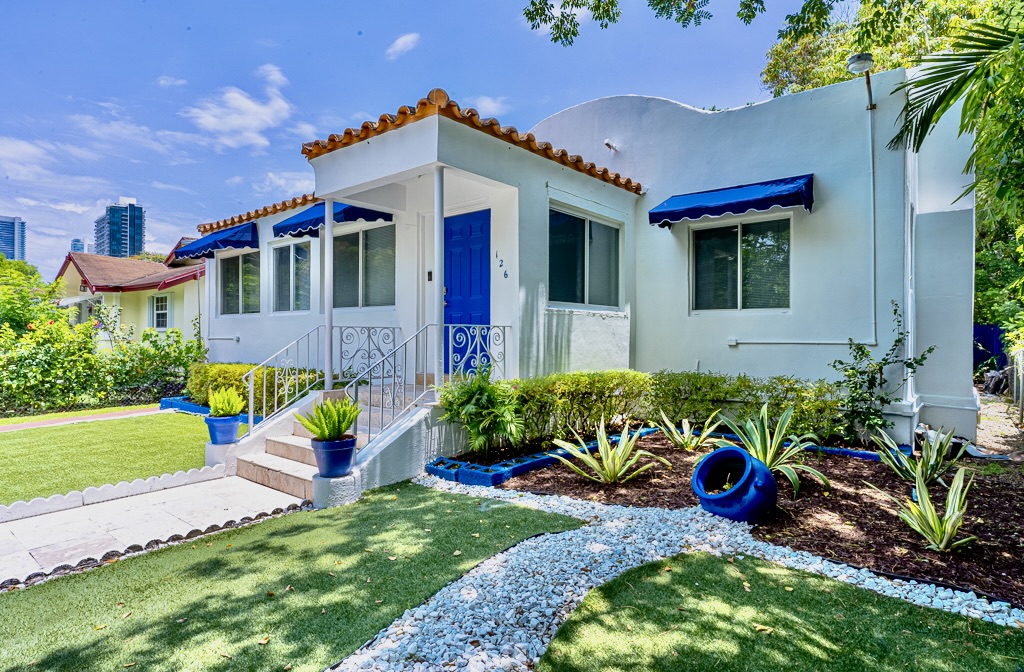
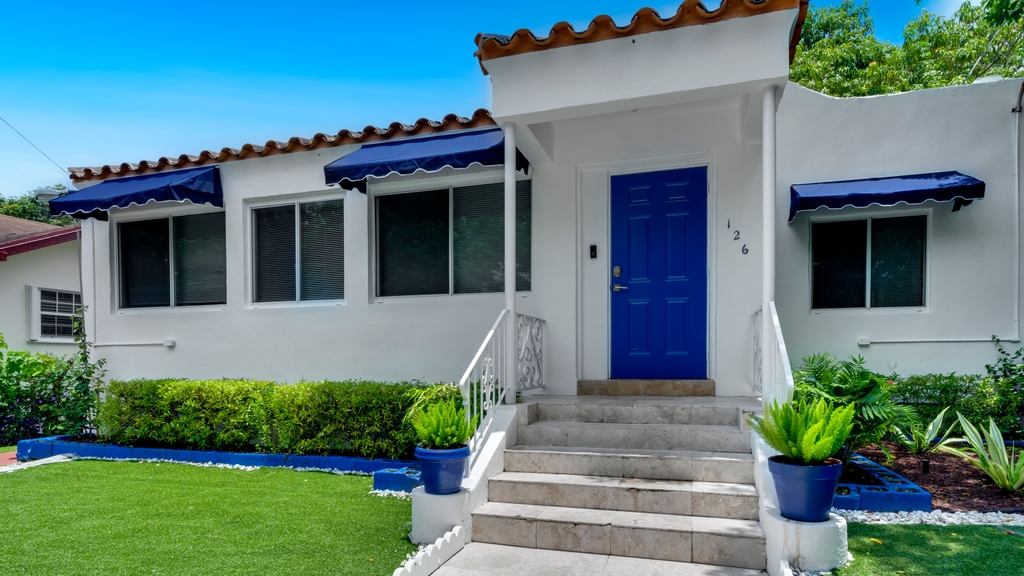
126 NW 33rd St, Miami-Dade County, Florida, 33127
Size: 1,822 sq. ft.
Price: $1,390,000
Income-Generating Wynwood Property
Seize the opportunity to own a prime property in Wynwood! This income-producing gem features a main house with 3 bedrooms, 2 bathrooms, plus a separate 1-bed, 1-bath guest house complete with its own kitchen and laundry amenities. Explore the potential of Airbnb and booking rentals, or dive into development with zoning for up to 17 units across four floors (T4R zoning). Located near Miami's top attractions, from the Design District to Brickell and Downtown, this property offers both immediate income and long-term development possibilities. Dive into Wynwood's dynamic real estate scene today!
200 South Andrews Avenue, 201, Broward County, Florida, 33301
Size:
Price: $24 per sq. ft. per annum
Museum Plaza - 2nd Floor
Seize a rare 5,675 SqFt office space on the second floor of Museum Plaza on Las Olas, 200 S Andrews Ave, in Downtown Fort Lauderdale's financial hub. Just a block from Las Olas Blvd, this Class A space is near government offices, courts, and universities. The 11-story building features sunlit interiors with large windows, a grand lobby with fine finishes, and modern elevators. Amenities include a parking garage with EV charging and a next door rooftop helipad. For lease or purchase, options include an option to buy. The unit has private offices with floor-to-ceiling windows and a central open space with wood-like floors, suitable for law firms, accountants, or light medical practices. It includes 10 offices and a conference room. A premier downtown opportunity.

200 South Andrews Avenue, 3rd Floor, Broward County, Florida, 33301
Size:
Price: $24 per sq. ft. per annum
Museum Plaza - 3rd Floor
Explore prime 16,048 SqFt office space on the third floor of Museum Plaza on Las Olas, 200 S Andrews Ave, in Downtown Fort Lauderdale's financial district. A block from Las Olas Blvd, near government buildings, courts, FAU, and Broward College, this 11-story building features a sunlit interior, a grand lobby with granite and marble, and updated elevators. It includes a next-door parking garage with EV stations and a next-door rooftop helipad. For lease or purchase, options include a full floor with modern, open-plan design, polished concrete floors, and glass walls, suitable for law firms, accountants, or light medical use. The customizable space offers private/shared offices and conference rooms. A distinguished choice in downtown. The property is offered for sale and lease.

9th Street, Miami, Florida, FL 12345
Size: 2,000 sq. mt.
Price: $50 per sq. mt. per annum
Warehouse
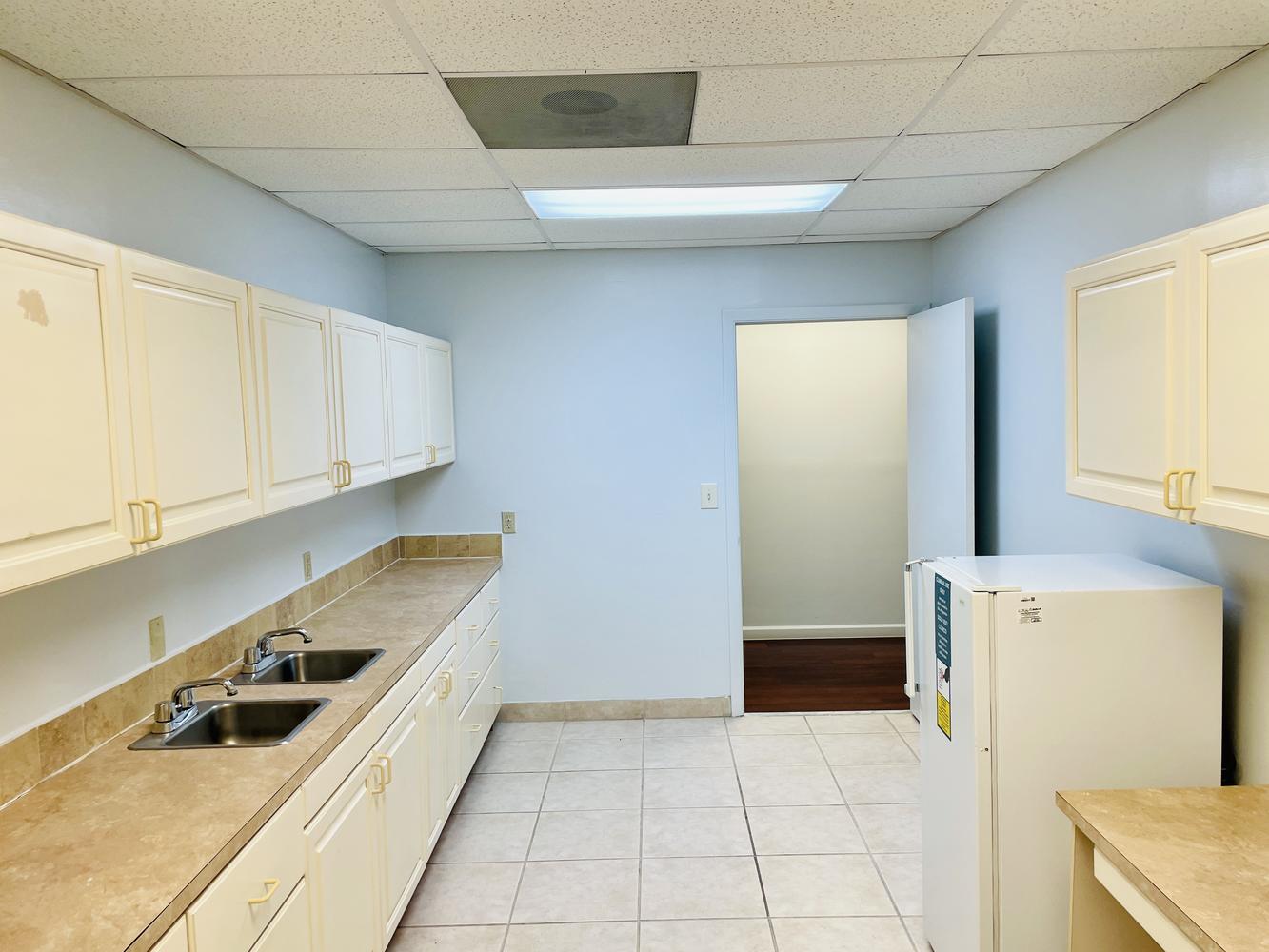
Looking for flexible warehouse space in Miami? Our fractional warehouse rental options allow you to share high-quality, secure storage and work space with other tenants at a fraction of the cost.
Modern Facility: Spacious, secure warehouse with loading docks and access to forklifts.
Long-Term Flexibility: Rent for the year and enjoy predictable, low overhead with shared use of space.
Prime Location: Centrally located in Miami with easy access to major highways, ports, and airports.
Shared Amenities: Utilities, security, and maintenance services included in your rent.
Additional Options: Ability to expand space or add equipment based on your needs.
Book your fractional warehouse space today and streamline your business operations in a convenient and cost-effective environment!
- Custom
Additional Space Deal: Rent a fractional space and add an extra 500 sq. ft. for free for the first 6 months.
- Rent
Early Bird Discount: Sign a yearly lease 3 months in advance and receive 10% off your first year’s rental.
Incentives

Ocean Drive, Miami, Florida, FL 12345
Size: 10 - 300 desks
Price: $200 - $350 per desk per month
Office Space for Rent by Desk
Looking for a professional workspace without the overhead? Our fractional office space in Miami offers the perfect solution! Rent by the desk on a monthly basis and enjoy a productive, collaborative environment.
Flexible Rentals: Rent individual desks per month, perfect for freelancers, startups, or remote teams.
Prime Location: Situated in the heart of Miami with easy access to transit, cafes, and business hubs.
Modern Amenities: High-speed internet, conference rooms, printers, and fully furnished workstations.
Collaborative Community: Network with like-minded professionals in a shared office setting.
All-Inclusive Pricing: Utilities, cleaning, and security included in your monthly rent.
Join a community of professionals in a dynamic office space – book your desk today!
- Custom
Referral Reward: Refer a colleague or business and both of you will receive $100 off your next month's rent.
- Rent
First-Month Discount: Get 15% off your first month’s desk rental!
- Service Charges
Long-Term Commitment Discount: Rent for 6+ months and receive a 10% discount on monthly service charges.
Incentives

Marina Lane, Miami, Florida, FL 12345
Size: 50 desks
Price: $3,000 per desk per annum
Luxurious Office
Elevate your workspace to a new level with our premium office space in Miami, available for annual desk rentals. Designed for professionals seeking a sophisticated, comfortable, and productive environment.
Prime Location: Situated in a prestigious Miami business district, close to dining, shopping, and transit.
Comprehensive Amenities: High-speed Wi-Fi, state-of-the-art conference rooms, 24/7 access, and personalized mail handling.
Professional Atmosphere: Network with top professionals in a vibrant yet exclusive setting.
All-Inclusive Package: Includes utilities, cleaning, and office supplies – no hidden fees.
Commit to excellence in a workspace that reflects your professional aspirations. Secure your desk today and work in luxury all year!
- Custom
Networking Perk: Receive complimentary access to exclusive office networking events during your first year.
- Rent
Group Desk Discount: Rent 3 or more desks together and get an additional 5% off each desk’s rental.
Early Renewal Bonus: Renew your lease 60 days before it expires and get one free month. - Service Charges
All-Inclusive Fee: Standard service charge of $120/month per desk covers utilities, high-speed internet, and cleaning.
Incentives

Lincoln Rd, Miami, Florida, FL 12345
Size: 2,800 sq. ft.
Price: $200,000 fixed price per annum
Bar
Step into history and charm with this old-style, cool bar available for annual lease. Perfect for entrepreneurs looking to create a distinctive nightlife experience, this venue offers vintage ambiance with modern convenience.
Classic Charm: Rustic interiors featuring exposed brick, wooden beams, and vintage decor.
Turnkey Ready: Fully equipped bar with seating, sound system, lighting, and kitchen space.
Prime Location: Situated in a lively Miami neighborhood with excellent foot traffic and visibility.
Customizable Space: Adaptable layout to suit your theme or event plans.
Ample Amenities: Includes on-site storage, restrooms, and staff facilities.
Don’t miss the chance to operate your dream bar in this iconic venue. Lease it for the year and bring your vision to life!
- Custom
Grand Opening Assistance: Receive free promotional support, including digital marketing and event planning, to help with your launch.
Decor Credit: Get a $1,000 credit towards customizing or refreshing the bar's vintage decor. - Rent
Multi-Year Commitment: Lock in your lease for 2 years and enjoy a 15% discount on the second year’s rent.
First-Month Free: Secure your annual lease and get your first month rent-free as a welcome bonus.
Incentives

Collins Ave., Miami, Florida, FL 12345
Size: 800 sq. ft.
Price: $800 fixed price per month
Five Stars Hotel Office Room
Elevate your business experience with our hotel office room, available for monthly rental. Perfect for remote work, small meetings, or traveling professionals, this private, fully furnished space combines luxury with functionality.
Private Workspace: A comfortable and quiet environment for work, calls, and meetings, offering complete privacy.
Modern Amenities: High-speed Wi-Fi, office desk, ergonomic chair, and a telephone line for business use.
Access to Hotel Services: Room service, on-site restaurant, fitness center, and concierge support for a convenient and efficient workday.
Prime Location: Located in a central area of Miami, with easy access to business districts, dining, and shopping.
Flexible Terms: Rent monthly for added flexibility without long-term commitments.
Rent your hotel office room today and enjoy the comfort and convenience of a professional, all-in-one workspace!
- Custom
Complimentary Breakfast: Enjoy a daily free breakfast at the hotel’s restaurant for the first 30 days of your rental (tea, or coffee included).
- Rent
First-Month Discount: Sign a 3-month lease and get 20% off the first month’s rent.
- Service Charges
All-Inclusive Monthly Fee: Standard service charge of $150 per month, which includes high-speed internet, cleaning, and utilities.
- Voucher
Incentives

How to list
Create your listing
It’s very simple, quick and easy to create an interesting, dynamic listing. To achieve the maximum success, please ensure all listings are complete with accurate and detailed information.
We also recommend professional photography as it enhances the quality of all listings.
Publish your listing
Once you have completed all the above steps you listing is ready to go live.
Check all details are accurate and correct and then hit the publish listing button and your listing is made live.
Manage your listing
You are in full control of all aspects of your listing.
You are able to create, edit and delete your listing at any time.
Please note: There is zero tolerance for false, misleading or inaccurate listings.
News & Articles
Custom Control, Maximum Exposure: Listing Tips for soCommercial – the marketplace for business space Users
Want to make your listing shine? Start with high-quality photos and clear, concise descriptions. Highlight unique features and amenities. Set competitive pricing based on time of day, demand, and local trends. Then, use soCommercial - the marketplace for business space’s built-in tools to create deals and offers. Promote your space on social media, and engage with inquiries quickly. The more active and responsive you are, the better your chances of getting booked. With soCommercial – the marketplace for business space, success is just a few clicks away. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
Success Stories: How Businesses Are Thriving with soCommercial – the marketplace for business space
From side-hustlers to seasoned entrepreneurs, soCommercial – the marketplace for business space users are turning space into success. Take the story of a café that opened its backroom for weekend workshops – booked solid for months. Or the event planner who rents out boutique showroom spaces on off-days. These stories are becoming more common, and they all started by listing on soCommercial – the marketplace for business space. Join the community of smart business owners making the most of their space. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
soCommercial – the marketplace for business space vs. Traditional Commercial Listings: What You Need to Know
Old-school commercial real estate sites are built for big deals and long leases. soCommercial - the marketplace for business space is different. It offers real-time control, flexibility, and tools for listing everything from a single chair to an event hall. Unlike traditional platforms, soCommercial - the marketplace for business space lets users create listings that match today's fast-moving, on-demand business environment. The result? Higher visibility, more bookings, and better returns for space owners. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
The Future of Flexible Space: Why soCommercial – the marketplace for business space Is Leading the Way
Work culture is changing. Businesses now seek adaptable, on-demand spaces over long-term leases. soCommercial - the marketplace for business space is at the forefront of this shift, making it easy to list, find, and book commercial spaces with unprecedented flexibility. From pop-up experiences to hybrid offices, the future belongs to agile businesses – and soCommercial – the marketplace for business space is their space partner. Join the movement that's reshaping how we work and rent. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
How soCommercial – the marketplace for business space Helps You Turn Idle Space Into Daily Income
Empty spaces are missed opportunities. With soCommercial – the marketplace for business space, every unused desk, meeting room, or lounge can become a daily revenue source. The platform allows you to monetize your idle areas, even for just a few hours a day. Over time, these small bookings add up to significant income. It’s passive revenue with active control – you decide when, who, and how your space gets used. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
The Easiest Way to List Commercial Property Online (Big or Small)
soCommercial - the marketplace for business space is designed to be user-friendly from start to finish. Whether you're listing a shared desk or an entire venue, the process is seamless. You don’t need technical knowledge or experience in commercial real estate. Just input the basics, upload a few photos, set your price, and go live. The platform's design guides you at every step, making listing your space intuitive and fast. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the marketplace for business space.
Custom Deals, Incentives & Offers: Stand Out on soCommercial – the marketplace for business space
Looking to attract more renters? soCommercial - the marketplace for business space gives you tools to create custom incentives and deals that stand out. Whether it's a "first day free" offer, seasonal discounts, or bundled packages for long-term use, these incentives increase engagement and conversions. You can tailor your promotions to specific user needs or trends in your area. Want to boost mid-week bookings? Offer a discount for Tuesday rentals. Need more weekend traffic? Launch a weekend-only bundle. The options are in your hands. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
List by the Hour, Day, or Week: Total Flexibility on soCommercial – the marketplace for business space
Traditional leases can be limiting, but soCommercial – the marketplace for business space changes the game. You can list your space for any timeframe – hourly, daily, weekly, or even just on weekends. This flexibility appeals to a wide range of renters, from yoga instructors needing a weekly class venue to startups looking for temporary project space. You choose the availability, the terms, and the price. With soCommercial – the marketplace for business space, flexible listings mean more visibility and more bookings. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
From Restaurant to Co-Working Hub: The Power of Repurposing with soCommercial – the marketplace for business space
Got a restaurant that sits empty during weekday mornings? A boutique that could host evening workshops? soCommercial - the marketplace for business space enables you to repurpose commercial spaces creatively and profitably. Repurposing allows you to turn quiet hours into revenue-generating opportunities. On soCommercial – the marketplace for business space, you can list your space for specific days and times, allowing full control over availability. Whether it's transforming a bar into a pop-up shop or a gallery into a meeting venue, the possibilities are endless. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
Maximize Every Square Foot: How soCommercial – the marketplace for business space Helps You Monetize Even the Smallest Space
In today's flexible economy, every square foot matters. soCommercial - the marketplace for business space empowers property owners to list spaces of all sizes-from a single desk to an entire office floor. Whether you're managing a large business center or simply have a corner in a shared office going unused, soCommercial – the marketplace for business space makes it simple to earn income from your idle space. With a few easy steps, you can post your space and start attracting freelancers, entrepreneurs, and small businesses looking for affordable and short-term rentals. soCommercial – the marketplace for business space's intuitive platform ensures even first-time users can get started quickly. Don't let space go to waste—maximize it with soCommercial – the marketplace for business space. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
How U.S. Interest Rates Are Shaping the Commercial Real Estate Market in 2025
As U.S. interest rates remain elevated in 2025, commercial real estate professionals, investors, and small business owners are closely watching how the market continues to respond. At soCommercial, we're seeing firsthand how these economic shifts are changing the way people list, lease, and monetize commercial spaces of all types. What’s Happening With U.S. Interest Rates? The Federal Reserve has maintained higher interest rates throughout early 2025 in an ongoing effort to control inflation. While these measures are helping stabilize consumer prices, they’ve also made borrowing more expensive — impacting financing for commercial property purchases, developments, and lease deals. The Ripple Effect on Commercial Real Estate Higher interest rates affect almost every corner of the commercial real estate ecosystem. Here’s how: 1. Reduced Transaction Volume With the cost of debt increasing, many investors are putting purchases on hold. This has slowed down overall transaction activity across office, retail, industrial, and hospitality sectors. However, that slowdown has created opportunities for creative leasing strategies and space repurposing, areas where platforms like soCommercial are thriving. 2. Shift Toward Leasing Over Buying Rather than taking on expensive financing, businesses are opting to lease space or share it. This has increased demand for flexible commercial leasing, especially fractional listings and short-term rentals, exactly what soCommercial is built for. From co-working desks to repurposed event spaces, users are listing underutilized assets and meeting this surge in demand. 3. Increased Popularity of Adaptive Reuse As financing new developments becomes more expensive, property owners are rethinking their strategies. Converting underperforming assets into new uses — like turning a vacant restaurant into a shared workspace is becoming a smart, cost-effective move. soCommercial makes it simple to list and promote these reimagined spaces. 4. More Creative Incentives and Deal Structures With leasing competition heating up, landlords and space owners are sweetening the deal. From rent-free periods to discounted service charges and QR-code promotions, flexible marketing strategies are driving results. soCommercial enables listers to build custom offers directly into their listings, increasing engagement and closing rates. Who’s Winning in This Market? Small and mid-sized operators who can move fast and think flexibly are outperforming traditional players. soCommercial users are leveraging the platform to: List spaces by the hour, day, or month Offer shared-use options like part-time clinics or hybrid venues Repurpose properties quickly based on market needs With many institutional players slowing down, there’s a growing space for entrepreneurs, startups, and individual landlords to gain ground The Future: Flexibility Is the New Currency As long as interest rates remain high, agility will be key in the commercial real estate world. Platforms like soCommercial are leading the way by: Simplifying space monetization Making commercial listings accessible to anyone Encouraging innovation through adaptive use and creative deals If you're looking to navigate the new landscape of commercial real estate in a high-rate environment, soCommercial is your competitive edge. Ready to List Smarter? Join thousands of users who are rethinking how commercial space works. Whether it’s a single desk, an empty storefront, or an entire building — you can list it, lease it, and monetize it on soCommercial. Get Started for Free Today This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
The Strategic Power of Deals and Incentives in Commercial Space Leasing
In a competitive real estate market, securing tenants is about more than just offering square footage. Today, deals and incentives are essential tools for creating compelling value propositions. Leading commercial real estate innovators like soCommercial are using creative leasing strategies to attract and retain high, quality tenants. From rent abatement and tenant improvement allowances to flexible lease terms and move, in bonuses, incentives help reduce barriers to entry and foster long, term relationships. They are especially effective in emerging neighborhoods or repositioned properties where attracting initial tenants is critical to building momentum. soCommercial tailors each deal package to the specific needs of the tenant and the market context. By understanding tenant personas and aligning with their operational goals, soCommercial crafts offerings that go beyond transactional leasing to build genuine partnerships. The strategic use of incentives also plays a key role in filling vacancies quickly and maintaining consistent cash flow. Whether it's a startup looking for its first headquarters or a growing business seeking regional expansion, the right deal can make all the difference. With its innovative, tenant, focused approach, soCommercial is redefining what it means to create win, win leasing agreements in the modern commercial real estate landscape. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
Transforming a Former Restaurant into a Thriving Co-Working Space
The repurposing of commercial spaces is not just a trend it’s a necessity in today’s fluid real estate environment. One of the most compelling examples of adaptive reuse is the conversion of former restaurants into co-working hubs. This innovative transformation is being led by forward by soCommercial, which specialize in breathing new life into obsolete properties. Restaurants typically come equipped with expansive dining areas, kitchens, restrooms, and sometimes even unique architectural features that make them ideal candidates for conversion. With strategic planning and thoughtful design, these spaces can be turned into vibrant co-working environments that foster creativity and collaboration. soCommercial approaches each transformation with a blend of practicality and vision. They assess the existing infrastructure, evaluate market demand, and implement renovations that maximize functionality while preserving character. The result is a cost, effective, eco, friendly solution that serves entrepreneurs, freelancers, and remote teams. By converting defunct eateries into modern workspaces, soCommercial supports urban revitalization and promotes more efficient use of commercial real estate. This approach also aligns with broader sustainability goals by reducing the need for new construction. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
Navigating the Factional Commercial Real Estate Market in the USA
The U.S. commercial real estate market is anything but monolithic. It is deeply factional, segmented by region, industry, asset type, and economic conditions. Understanding these factions is key to navigating opportunities and mitigating risks in this complex sector. soCommercial plays a pivotal role in bridging these divisions, providing tailored solutions that align with the unique dynamics of each submarket. From tech hubs in San Francisco and Austin to logistics strongholds in the Midwest, each region presents its own set of opportunities and challenges. Economic indicators, demographic trends, and local policy decisions all influence the viability and value of commercial properties. For example, while downtown office space in large metros may be experiencing a downturn, suburban office parks and industrial warehouses are seeing a boom. soCommercial leverages hyperlocal markets and uses its flexible marketplace to enable stakeholders tap into different markets. For all stakeholders and business owners, using soCommercial is a great way to quickly revitalize spaces through either repurposing term or offering custom deals and incentives. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
The Evolving Landscape of Commercial Space Usage in the USA
As businesses continue to redefine how and where they operate, the commercial real estate landscape in the United States is undergoing a dramatic transformation. From retail storefronts to office high rises, the demand for adaptable, flexible, and sustainable spaces is reshaping the market. At the forefront of this transformation is soCommercial, a brand committed to reimagining and repurposing commercial spaces to meet modern demands. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated trends toward remote work, e-commerce, and decentralized operations. This shift has led to declining demand for traditional office and retail spaces while sparking interest in mixed, use developments, co-working environments, and niche commercial applications such as fulfilment centers and content studios. soCommercial enables underutilized properties to be quickly and easily re-purposed into fresh into vibrant, functional spaces tailored to the needs of startups, creative professionals, and remote teams. By doing so, they not only support economic revitalization in urban and suburban areas but also help build a more resilient commercial ecosystem. Flexible lease terms, smart building technologies, and community, centered amenities are increasingly becoming standard. Businesses are not just looking for space; they are seeking environments that support productivity, collaboration, and employee wellbeing. With its data driven approach and commitment to design excellence, soCommercial is setting new standards in commercial space innovation. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
Analyzing the Impact of Changing Uses in Commercial Real Estate Across U.S. States
SoCommercial believes that the shifting dynamics of commercial real estate across the United States are reshaping the industry’s landscape. This transformation stems from evolving economic trends, demographic shifts, and technological advancements, which have impacted different states in varied ways. By examining the changing uses of commercial real estate, we can understand the states most affected and the reasons behind these shifts. The Driving Forces Behind the Changes Several key factors are driving the transformation of commercial real estate: Remote Work and Office Space Decline The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed a rapid adoption of remote work. As a result, many businesses have downsized their physical office spaces, leading to a surplus of office buildings in urban centers. E-Commerce Boom The rise of online shopping has shifted demand from traditional retail spaces to industrial real estate, such as warehouses and distribution centers. Population Shifts Migration trends, particularly from high-cost coastal cities to more affordable regions, have influenced real estate markets. States with growing populations see increased demand for mixed-use developments that combine residential, commercial, and recreational spaces. Sustainability and Technology The push for green buildings and smart technology integration has altered the design and use of commercial properties. States Most Impacted by the Changes While these trends have affected the entire country, some states stand out due to the magnitude and nature of the changes: California California, a historical hub for technology and innovation, has experienced a significant shift in commercial real estate. High costs of living and business operations have prompted many companies to downsize or relocate. The Bay Area, in particular, has seen an exodus of tech firms moving to states like Texas and Florida, leaving behind vacant office spaces. Texas In contrast, Texas has emerged as a beneficiary of these shifts. Cities like Austin and Dallas have become hotspots for corporate relocations, driving demand for office spaces, industrial properties, and mixed-use developments. The state’s business-friendly environment and affordable living costs make it attractive for both companies and workers. New York New York’s commercial real estate market has been hit hard, particularly in Manhattan. The decline in demand for office spaces and the slow recovery of the retail sector have left landlords struggling to adapt. However, the city’s resilience lies in its capacity for reinvention, with a focus on converting office buildings into residential or mixed-use properties. Florida Florida has seen a surge in demand for commercial real estate, fueled by population growth and an influx of businesses. Miami, in particular, has become a hub for fintech and other industries, driving demand for modern office spaces and co-working environments. Midwestern States States like Ohio and Indiana have experienced growth in industrial real estate due to their central locations and accessibility to transportation networks. The shift toward e-commerce has led to a boom in warehouses and distribution centers in these areas. Why These States Have Been Most Affected The impact on these states can be attributed to several factors: Economic Policies States with favorable tax policies and incentives for businesses have seen increased investment in commercial real estate. Population Growth: Regions experiencing an influx of residents require new infrastructure, including retail spaces, offices, and mixed-use developments. Industry Presence: States with thriving industries, such as tech in Texas and finance in Florida, have experienced tailored demand for specific types of properties. Cost of Living and Quality of Life: Affordability and lifestyle amenities attract workers and businesses alike, shifting the demand for commercial spaces. The Road Ahead SoCommercial believes that the ongoing evolution of commercial real estate is a reflection of broader societal changes. While some states grapple with declining office occupancy and retail closures, others are capitalizing on the rise of remote work and e-commerce. The key for stakeholders is to adapt to these changes by repurposing properties, embracing sustainability, and leveraging technology to meet the needs of a dynamic market. As the commercial real estate landscape continues to shift, the industry’s future will depend on its ability to innovate and respond to these transformative trends. By staying attuned to the unique challenges and opportunities in each state, businesses and investors can navigate this evolving terrain with confidence. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
The changing face of Florida's commercial real estate market: 2000 to 2024
The Florida commercial real estate market has undergone significant transformations since the turn of the 21st century. As one of the fastest-growing states in the U.S., Florida’s evolution in demographics, economic drivers, technology, and market dynamics have reshaped its commercial real estate landscape. This article explores the factors influencing these changes over the last two decades, focusing on population growth, shifts in market demand, technological advancements, and the growing emphasis on sustainability. Population growth and urbanization One of the most significant factors shaping Florida’s commercial real estate market is its population growth. Between 2000 and 2023, Florida’s population surged from approximately 16 million to over 22 million, making it the third most populous state in the U.S. The state’s attractive climate, lack of state income tax, and reputation as a retirement haven have drawn both retirees and younger, economically active populations from across the country. This population growth has driven demand for diverse commercial real estate assets, particularly in major urban centers like Miami, Tampa, Orlando, and Jacksonville. While the early 2000s saw suburban expansion, the past decade has been marked by a trend toward urbanization, with mixed-use developments and urban infill projects catering to a growing preference for live-work-play environments. Tourism and retail evolution Florida’s tourism industry has long been a pillar of its economy, with destinations like Disney World, Miami Beach, and the Florida Keys attracting millions of visitors annually. However, the nature of retail and hospitality assets has evolved significantly since 2000. The early 2000s were dominated by the construction of large retail centers and malls. However, with the rise of e-commerce and changing consumer habits, many traditional malls faced decline or repurposing in the 2010s. Developers pivoted to open-air shopping centers, entertainment districts, and mixed-use developments. Tourist-centric retail spaces such as the Miami Design District and ICON Orlando have emerged as experiential destinations combining luxury retail, dining, and entertainment. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated some of these shifts, leading to the repurposing of retail spaces for last-mile logistics centers, ghost kitchens, and other uses aligned with the digital economy. The hospitality sector, initially devastated by the pandemic, has rebounded strongly, with renewed investment in boutique hotels and short-term rental properties catering to changing traveler preferences. The rise of industrial real estate One of the most dynamic areas of Florida’s commercial real estate market has been the rise of industrial real estate. Fueled by the growth of e-commerce and Florida’s strategic location as a gateway to Latin America and the southeastern U.S., demand for warehouse and logistics facilities has soared. Major infrastructure investments, including the expansion of the Panama Canal and improvements to Florida’s ports in Miami, Tampa, and Jacksonville, have bolstered the state’s role in global trade. This, in turn, has spurred the development of industrial hubs around key transportation corridors. As of 2023, the industrial sector is among the fastest-growing asset classes in Florida, with vacancy rates at historic lows and rental rates climbing steadily. Office market transformations The Florida office market has undergone a profound transformation over the past two decades, reflecting broader economic trends and workplace changes. In the early 2000s, office development centered on suburban business parks. However, as Florida’s cities became more cosmopolitan, demand shifted toward urban office spaces in vibrant downtown areas. The rise of remote and hybrid work models, accelerated by the pandemic, has created challenges for traditional office spaces. Many companies downsized or reconfigured their office footprints to accommodate flexible work arrangements. In response, developers have increasingly focused on adaptive reuse projects, converting outdated office buildings into residential or mixed-use spaces. The tech sector’s growth in cities like Miami, buoyed by an influx of entrepreneurs and venture capital, has added a new layer of demand for modern, high-tech office spaces. Co-working spaces, once niche, have also become a fixture in Florida’s commercial real estate market, catering to startups and remote workers. Multifamily housing as a commercial asset While traditionally considered a residential asset, multifamily housing has become a cornerstone of Florida’s commercial real estate market. The influx of new residents, coupled with rising home prices, has fueled demand for rental properties. Institutional investors have increasingly targeted Florida’s multifamily market, attracted by strong rent growth and low vacancy rates. Developments have evolved to include luxury apartments, affordable housing projects, and workforce housing to accommodate a diverse renter base. Cities like Orlando and Miami have seen a proliferation of high-rise multifamily developments, often integrated with retail and office spaces. Sustainability and resilience Florida’s susceptibility to hurricanes, flooding, and rising sea levels has made sustainability and resilience critical considerations for commercial real estate. Since 2000, the state has adopted stricter building codes and incentivized sustainable construction practices. Developers increasingly incorporate green building certifications such as LEED into projects, and resilient design features—like elevated structures, floodproofing, and renewable energy systems—have become standard in coastal areas. This focus on resilience has also influenced investment patterns. Institutional investors now assess climate risks more rigorously, and some are favoring inland areas over vulnerable coastal regions. The role of technology Technology has been a game-changer for Florida’s commercial real estate market. Innovations in construction technology, property management, and data analytics have streamlined operations and improved efficiency. Proptech platforms have made it easier for investors to analyze market trends, while smart building technologies enhance tenant experiences and reduce operating costs. Florida’s emergence as a tech hub, particularly in Miami, has also contributed to the market’s dynamism. The influx of tech companies and remote workers has driven demand for modern office spaces, high-speed internet infrastructure, and amenities catering to a tech-savvy population. Investment trends and outlook Florida’s commercial real estate market has attracted substantial domestic and international investment over the past two decades. While the early 2000s were characterized by speculative development, the market has matured, with investors focusing on long-term value and stable income-producing assets. The rise of private equity and real estate investment trusts (REITs) has also played a significant role, bringing institutional capital into Florida’s market. Cities like Miami have become global investment destinations, attracting capital from Europe, Latin America, and Asia. Looking ahead, Florida’s commercial real estate market is poised for continued growth. The state’s favorable tax environment, population growth, and economic diversification provide a strong foundation for future development. However, challenges such as climate change, affordability, and infrastructure constraints will require innovative solutions from policymakers and industry stakeholders. Conclusion The Florida commercial real estate market has undergone a remarkable transformation since 2000, driven by population growth, shifting economic trends, and evolving consumer preferences. From the rise of industrial real estate to the reinvention of retail and office spaces, the market reflects the dynamic interplay of local and global forces. As Florida continues to grow and evolve, its commercial real estate sector will remain a bellwether for broader economic and social trends, offering both challenges and opportunities for investors, developers, and communities. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
Maximizing profit: the commercial opportunity of shared commercial spaces
In a rapidly evolving economy, the adage "less is more" has taken on a new meaning in the realm of commercial real estate. Businesses and property owners are increasingly recognizing the untapped potential of underutilized commercial spaces. Whether it's an office with too many empty desks, a retail store with underused backrooms, or a restaurant with downtime during the day, sharing commercial spaces has emerged as a lucrative and sustainable model. This trend is redefining how businesses think about property utilization, creating new revenue streams while fostering collaboration and innovation. The case for sharing commercial spaces The concept of shared spaces isn't new. Co-working spaces, such as WeWork and Regus, have been pioneers in turning vacant offices into thriving hubs for freelancers, startups, and remote workers. However, the model has now expanded beyond co-working to encompass a wider variety of commercial settings. The driving forces behind this shift include rising real estate costs, changing work patterns, and a growing focus on sustainability. Rising real estate costs Commercial property prices and rents have been steadily increasing, particularly in urban areas. For many businesses, owning or leasing a space is a significant financial burden, often leaving them with little choice but to leave parts of their property unused. Sharing spaces can offset these costs by generating additional income from tenants who need temporary or flexible arrangements. Changing work and consumer patterns The pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work, e-commerce, and flexible schedules, leaving many traditional offices and retail spaces partially empty. These shifts have created an opportunity to rethink how spaces are used. For instance, an office could rent out unused meeting rooms to small businesses, or a retail store could lease its storage area to an online retailer needing a distribution point. Sustainability and efficiency Environmental concerns are another driving factor. Sharing spaces promotes better resource utilization, reducing the need for new construction and the associated environmental impact. By maximizing the use of existing infrastructure, businesses can lower their carbon footprints and align with growing consumer demand for sustainable practices. Opportunities across industries The potential for shared commercial spaces spans multiple industries, each with its unique set of opportunities. Retail Retailers can transform underutilized floor space into revenue-generating areas. For example, a boutique might host pop-up shops for emerging brands or rent space to local artisans. These arrangements not only generate income but also draw new customers, creating a win-win situation. Hospitality Restaurants and cafes, which often experience downtime during non-peak hours, can lease their spaces for events, workshops, or even co-working. Similarly, hotels can rent out conference rooms or unused spaces to small businesses or community groups. Offices With hybrid work models becoming the norm, many companies find themselves with surplus office space. By partnering with co-working operators or offering short-term leases to freelancers and startups, these companies can turn empty desks and meeting rooms into steady revenue streams. Warehousing and logistics As e-commerce continues to grow, the demand for storage and distribution hubs has surged. Businesses with spare warehouse space can lease it to smaller companies needing storage solutions, particularly in prime urban locations where logistics facilities are in high demand. The rise of technology-driven solutions Technology plays a crucial role in enabling the sharing of commercial spaces. soCommercial now makes it super easy for property owners and stakeholders to list available spaces and for businesses to find and book them. These digital marketplaces streamline the process, offering features like flexible booking, transparent pricing, and user reviews. In addition to listing platforms, property management tools equipped with data analytics can help businesses track space usage, identify inefficiencies, and determine the best opportunities for sharing. For example, sensors and smart software can monitor foot traffic and occupancy, providing insights into when and where space is being underutilized. Benefits beyond revenue While the financial benefits of sharing commercial spaces are clear, the advantages extend far beyond the bottom line. Community building Sharing spaces fosters collaboration and builds a sense of community among businesses and individuals. This can lead to partnerships, networking opportunities, and even customer growth as businesses cross-promote to each other's audiences. Flexibility and scalability For startups and small businesses, shared spaces offer an affordable and low-risk way to access premium locations without committing to long-term leases. This flexibility can be a game-changer, allowing businesses to scale up or down based on demand. Innovation and creativity Mixing diverse businesses in shared spaces often sparks innovation. For example, a graphic design studio renting space from a marketing firm could lead to collaborative projects and fresh ideas. Challenges and considerations While the benefits are significant, sharing commercial spaces does come with challenges. Property owners and tenants must navigate potential conflicts over usage, maintenance, and liability. Clear agreements and transparent communication are essential to ensuring a smooth partnership. Regulatory hurdles can also pose obstacles. Zoning laws and building codes may limit how spaces can be used or require additional permits. Businesses must be proactive in understanding and complying with these regulations. Finally, not all spaces are suited for sharing. Factors such as location, accessibility, and amenities play a crucial role in determining whether a space can attract tenants or partners. The path forward As the sharing economy continues to expand, the concept of shared commercial spaces is poised to become a mainstream business strategy. Property owners who embrace this model can unlock new revenue streams, while businesses seeking flexible solutions can access premium spaces at lower costs. Moreover, the emphasis on sustainability and community-building aligns with broader societal trends, making this approach not just profitable but also socially responsible. For companies and entrepreneurs looking to explore this opportunity, the key is to think creatively and strategically about how their spaces can serve others. Whether it's a corner office, a storage room, or a dining area, every square foot holds the potential to create value. In an era where adaptability is paramount, sharing commercial spaces offers a compelling solution to maximize resources and drive growth. It’s not just about filling empty rooms—it’s about transforming the way we think about space, collaboration, and the future of business. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
The rise of flexible commercial spaces: a creative approach to commercial real estate
The commercial real estate landscape is undergoing a seismic shift. Gone are the days when single-use, single-purpose buildings dominated the market. The demand for versatile, flexible spaces that can cater to a variety of needs has emerged as a defining trend, driven by changes in work culture, consumer behavior, and economic imperatives. This evolution requires creativity and strategic planning to ensure that commercial spaces remain relevant and profitable in an increasingly dynamic market. The forces driving change Several key factors are propelling the transition away from traditional, purpose-specific buildings toward multi-use, adaptable spaces: Shifts in work culture The rise of hybrid work models and remote work has diminished the demand for conventional office spaces. Instead, businesses seek dynamic environments that can flex between co-working hubs, meeting venues, and collaboration zones. This shift challenges traditional office building designs and demands innovative reconfigurations to optimize utility. Changing retail landscape E-commerce's exponential growth has disrupted the retail sector, leaving many brick-and-mortar stores struggling. As a result, retail spaces are increasingly being repurposed for alternative uses such as fitness centers, popup shops, or entertainment venues. This trend is especially pronounced in shopping malls, which are reimagining themselves as multi-use hubs with residential, retail, and recreational spaces under one roof. Urbanization and space efficiency In densely populated urban areas, the scarcity of land makes multi-purpose spaces more economically viable. Mixed-use developments, combining residential units, offices, and retail outlets, are becoming the norm. This approach maximizes land use while fostering vibrant, 24/7 communities. Economic resilience Multi-use properties offer a financial hedge for investors and developers. Diversified revenue streams from tenants in different industries reduce the risk of vacancies tied to market downturns in a single sector. Creative repurposing: the key to unlocking potential The pivot toward flexible commercial spaces necessitates out-of-the-box thinking. Developers and property managers must creatively reimagine how their spaces can serve diverse purposes. Here are some approaches that have proven successful: Adaptive reuse Transforming obsolete structures into modern, multi-purpose spaces is a popular strategy. For example, old warehouses are being converted into trendy co-working spaces or art galleries. Similarly, vacant big-box stores are being adapted into logistics hubs, healthcare clinics, or even residential units. Pop-up opportunities Pop-up installations allow businesses to test ideas or operate in a space temporarily, often without requiring significant structural changes. This trend has proven successful in retail, food and beverage, and even experiential marketing events. Technology-driven flexibility Smart building technologies, including modular walls and multi-functional furniture, enable spaces to be easily reconfigured to meet changing needs. A conference room today can serve as a yoga studio tomorrow, thanks to these innovations. Community-centric design Mixed-use developments that incorporate communal amenities—like green spaces, shared kitchens, or event venues—create vibrant ecosystems that appeal to a wide demographic. These designs ensure steady foot traffic and enhance tenant satisfaction. Future Considerations As the trend toward flexible commercial spaces accelerates, developers and stakeholders must address key challenges: Balancing cost and creativity While innovative designs and repurposing projects can be lucrative, they often come with high initial costs. Striking the right balance between investment and potential returns is critical. Navigating zoning and regulations Many urban areas still operate under zoning laws that were written with single-use buildings in mind. Policymakers and developers must collaborate to modernize regulations that allow for more creative, multi-use developments. Sustainability as a priority Sustainable design is no longer optional. From energy-efficient materials to eco-friendly construction practices, the demand for green spaces is shaping the future of commercial real estate. Flexible spaces that prioritize sustainability will have a competitive edge. Conclusion The shift toward flexible commercial spaces represents an exciting evolution in real estate. By embracing adaptability and creative design, developers can future-proof their investments while meeting the diverse needs of modern businesses and communities. As the lines between work, play, and living continue to blur, the demand for spaces that reflect this fluidity will only grow. The key to success lies in bold innovation and a willingness to reimagine what a commercial space can be. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
The decline of traditional leases: embracing the simplicity of flexible hybrid workspaces
The commercial real estate industry is undergoing a profound transformation as traditional long-term leases give way to the rise of flexible hybrid workspaces. This shift, driven by changes in workplace culture, technological advancements, and economic pressures, has ushered in a new era where simple agreements, rather than multi-page legal contracts, define the leasing process. For real estate professionals, this evolution represents both a challenge and an opportunity to adapt to the changing demands of tenants. The fall of the traditional lease For decades, the commercial real estate market relied on multi-year leases that required significant legal involvement. These agreements were often cumbersome, involving: Extensive negotiations between tenants and landlords. Complex legal language requiring interpretation by attorneys. Significant upfront costs, including legal fees and security deposits. Rigidity, locking tenants into spaces that might no longer meet their needs as businesses evolved. However, this traditional leasing model is increasingly at odds with today’s fast-paced, technology-driven business environment. Companies now prioritize flexibility, scalability, and simplicity, making the old leasing model appear antiquated. The drivers behind the shift Several factors have contributed to the decline of traditional leases: The Rise of Hybrid Work Models The pandemic permanently altered how people work. Remote work and hybrid models have become the norm, reducing the need for large, static office spaces. Businesses no longer want to commit to 10-year leases for offices they may not fully utilize. Instead, they seek: Short-term agreements that allow for scaling up or down. Access to shared spaces for occasional in-person collaboration. A focus on amenities that enhance employee well-being and productivity. Economic Uncertainty The global economy has experienced significant turbulence in recent years, from the pandemic to inflation and market volatility. Businesses are reluctant to take on long-term financial commitments like traditional leases when flexibility can offer cost savings and agility. Technology and the Gig Economy Advances in technology have made it possible for businesses to operate from virtually anywhere. Additionally, the rise of the gig economy means a growing number of entrepreneurs, freelancers, and small businesses require flexible workspace solutions rather than traditional leases. The Evolution of Real Estate Offerings Providers of coworking and flexible office spaces, such as WeWork, Industrious, and Regus, have set a new standard for how commercial spaces are leased. These providers offer month-to-month agreements or short-term contracts with minimal legal requirements, reshaping tenant expectations across the industry. Flexible hybrid workspaces: the new norm Flexible hybrid workspaces represent a radical departure from traditional leasing models. These spaces are designed to accommodate changing business needs, providing tenants with the ability to scale their usage up or down as required. The hallmarks of this model include: Simplicity Leases are often reduced to one or two pages, eliminating the need for extensive legal review. Ease of Entry Tenants can often secure space with minimal upfront costs and a quick approval process. Flexibility Agreements are typically month-to-month or short-term, allowing businesses to adapt as needed. Turnkey Solutions These spaces are move-in ready, often furnished and equipped with high-speed internet, shared meeting rooms, and other amenities. Community and Networking Opportunities Hybrid workspaces foster collaboration and networking among tenants, creating a vibrant ecosystem of businesses. Why simple agreements work One of the most attractive aspects of flexible workspaces is the simplicity of their agreements. These agreements are typically designed to be: Transparent Clear, straightforward terms reduce the risk of disputes and misunderstandings. Efficient Without the need for extensive legal negotiation, deals can be closed quickly. Cost-Effective Businesses save on legal fees and other costs associated with traditional leasing. For landlords and space providers, these simplified agreements streamline operations and attract a broader range of tenants, from startups to established enterprises. The legal implications: do we still need lawyers? While flexible workspace agreements significantly reduce the need for legal involvement, they don’t eliminate it entirely. Legal expertise remains valuable for: Ensuring compliance with local regulations and zoning laws. Protecting landlords and tenants from liability. Drafting master agreements that can be easily customized for individual tenants. However, the reduced complexity of these agreements means that legal costs are significantly lower, benefiting both parties. Challenges and considerations for real estate developers The transition to flexible hybrid workspaces presents challenges for developers accustomed to traditional leasing models. Key considerations include: Revenue Predictability Short-term agreements can create revenue volatility compared to the steady income of long-term leases. Developers must find ways to balance flexibility with financial stability. Space Utilization Efficiently managing shared spaces, such as meeting rooms and common areas, is critical to ensuring tenant satisfaction and maximizing profitability. Differentiation As the market for flexible workspaces grows, developers must offer unique amenities and services to stand out. This might include wellness programs, state-of-the-art technology, or premium locations. Scalability Developers need to design spaces that can be easily reconfigured to meet changing tenant demands, from private offices to open coworking areas. The future of leasing: a win-win for tenants and landlords The move toward flexible hybrid workspaces reflects a broader trend of consumer-centric real estate. Tenants benefit from the freedom and agility to operate on their terms, while landlords attract a diverse pool of tenants and reduce vacancy rates. This new model also aligns with broader societal shifts toward minimalism and sustainability. Smaller, more efficient office spaces reduce waste and carbon footprints, aligning with the values of modern businesses and employees. Conclusion The era of traditional leases is rapidly fading, replaced by the simplicity and flexibility of hybrid workspaces. For real estate developers, this is an opportunity to innovate and meet the needs of a dynamic, evolving market. By embracing short-term agreements, turnkey solutions, and tenant-friendly practices, developers can position themselves for success in this new landscape. As the industry continues to evolve, one thing is clear: simplicity, flexibility, and adaptability are no longer optional—they are the keys to the future of commercial real estate. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.
Adapting to evolving commercial space needs in Florida: 2019 to 2024
Over the past five years, the landscape of commercial real estate in Florida has undergone significant transformation. Shifts in consumer behaviors, technological advancements, and global events like the COVID-19 pandemic have altered the demands for office spaces, hospitality venues, leisure facilities, and medical centers. For real estate developers, understanding these trends is crucial to creating adaptable, profitable, and future-ready spaces. 1. Office spaces: from traditional to hybrid work models The office sector has experienced a seismic shift, driven by the rise of hybrid work models. Pre-2020, Florida’s thriving business hubs, such as Miami, Tampa, and Orlando, saw steady demand for traditional office spaces. However, the pandemic accelerated remote working, leading to a reevaluation of office requirements. Key trends include: Flexible office designs Companies now prefer adaptable layouts that accommodate in-person collaboration, hot-desking, and private meeting spaces. Co-working spaces, such as WeWork and Industrious, continue to expand to cater to startups and freelancers. Suburban growth Suburban office developments are in higher demand as employers seek to reduce commutes and align with employees' preferences for work-life balance. Technology integration Smart offices with robust internet infrastructure, touch-less entry, and wellness features are now standard expectations. 2. Hotels and hospitality: experiential and sustainable focus Florida's tourism industry remains a cornerstone of its economy, but travelers' expectations have evolved. Post-2019, there’s a greater emphasis on health, wellness, and unique experiences. Experiential stays Boutique hotels and themed accommodations are thriving as travelers seek more personalized and memorable stays. Properties near natural attractions, such as the Everglades or Florida Keys, are particularly popular. Wellness tourism Wellness-oriented resorts offering spa services, yoga retreats, and eco-conscious amenities have grown. Sustainability Developers are incorporating green building practices, energy-efficient systems, and sustainable landscaping to appeal to eco-conscious travelers and meet state regulations. 3. Leisure: mixed-use developments lead the way The leisure industry has seen a convergence of retail, dining, and entertainment in mixed-use developments. Projects like Miami's Brickell City Centre and Tampa's Water Street reflect this trend. Family-friendly venues Developers are investing in spaces that cater to multigenerational audiences, such as arcades, bowling alleys, and escape rooms, integrated with dining and shopping options. Outdoor spaces Outdoor dining, live music venues, and open-air markets surged in popularity during the pandemic and remain a draw for residents and tourists alike. Event-ready spaces Florida’s role as a destination for conferences and events has revived interest in adaptable venues that can host both large gatherings and intimate experiences. 4. Restaurants and bars: a new age of dining Florida’s dining scene has pivoted toward innovative formats and customer-focused offerings. Casual dining dominance Fast-casual and quick-service restaurants have outperformed traditional sit-down establishments due to convenience and affordability. Ghost kitchens The rise of delivery apps has fueled demand for ghost kitchens—commercial kitchens without customer-facing dining areas—especially in urban centers. Experiential dining Themed restaurants and bars that offer interactive experiences, such as rooftop bars or speakeasies, are drawing clientele seeking entertainment alongside their meals. Outdoor dining Permanent outdoor dining areas, initially a pandemic measure, have become a long-term feature for many establishments. 5. Medical centers: growth fueled by demographics and technology Florida's growing and aging population has heightened demand for medical facilities. Advances in healthcare technology and a focus on patient-centered care are shaping the development of these spaces. Outpatient centers Freestanding emergency rooms and outpatient clinics are being prioritized over traditional hospital expansions due to cost efficiency and convenience. Specialized facilities Developers are investing in specialized facilities, such as oncology centers, diagnostic labs, and mental health clinics. Telemedicine infrastructure Medical offices now require enhanced technological capabilities to support telemedicine consultations and digital health monitoring systems. 6. Mixed-use and transit-oriented developments An overarching trend across all sectors is the rise of mixed-use developments, particularly those near transit hubs. These projects integrate residential, commercial, and leisure spaces, creating vibrant communities where people can live, work, and play without excessive commuting. Adaptability is key Spaces that can be reconfigured for multiple uses will retain value and relevance in the face of market changes. Technology and sustainability Smart building features and eco-friendly practices are now competitive necessities. Community-centric design Projects that prioritize community engagement and offer diverse amenities will appeal to Florida's dynamic and growing population. The commercial real estate market in Florida remains robust, but the priorities of tenants and end-users have shifted. Developers who can anticipate and adapt to these evolving needs will be well-positioned for success in the years ahead. This article was commissioned by soCommercial – the market place for business space.